Figure 3.
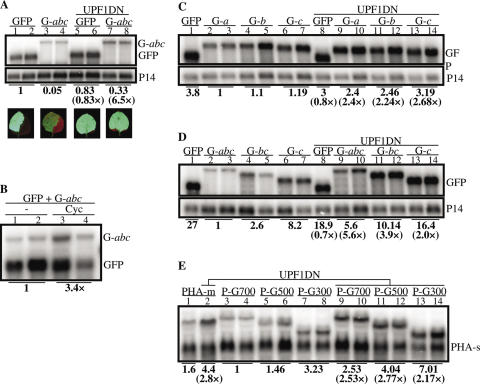
Long 3′-UTR acts as NMD cis element. (A) Accumulation of GFP and GFP-abc (shown as G-abc) mRNAs in leaves of N.benthamiana that were infiltrated with GFP + P14 (lanes 1 and 2), GFP-abc + P14 (lanes 3 and 4), GFP + P14 + UPF1DN (lanes 5 and 6) or GFP-abc + P14 + UPF1DN (lanes 7 and 8) cultures. RNA gel blot was hybridized first with a GFP probe (upper panel), then it was reprobed with P14 (lower panel). GFP and GFP-abc transcript levels were normalized to P14 mRNA levels. Mean GFP transcript level was taken as 1 (bold number below lower panel) and the test (GFP or GFP-abc) mRNA levels of other samples are shown relative to it. Bracketed numbers (lanes 5–6 and lanes 7–8) refer to the fold change of test transcript levels in the presence of UPF1DN relative to the corresponding mRNA levels obtained in the absence of UPF1DN. Photos show the GFP activity in the infiltrated leaves. (B) Effect of cycloheximide (Cyc) on the accumulation of GFP and GFP-abc (shown as G-abc) transcripts in N.benthamiana leaves. RNA gel blot was hybridized with a GFP probe. (C) DSE-like destabilizing sequences could not be found in the abc region. GFP, GFP-a (G-a), GFP-b (G-b) and GFP-c (G-c) mRNA levels were normalized to the corresponding P14 mRNA levels. Mean GFP-a transcript level is taken as 1. GFP, GFP-b and GFP-c transcript levels are shown relative to the level of GFP-a. Bracketed numbers show the fold change of corresponding test transcript levels in the presence of UPF1DN. Blot was hybridized first with the GFP probe (upper panel), then it was reprobed with P14 (lower panel). (D) The length of the 3′-UTR defines the efficacy of NMD. GFP-abc (G-abc), GFP-bc (G-bc), GFP-c (G-c) and GFP mRNA levels were normalized to the corresponding P14 levels, and the mean GFP-abc transcript level was taken as 1. (E) Bacterial sequences inserted into the 3′-UTR of a plant mRNA triggers NMD. The length of the inserted bacterial sequences is in correlation with the intensity of NMD. 700, 500 or 300 nt sequences from GUS gene were inserted downstream of the stop codon of PHA-s (P-G700, P-G500 and P-G300). P-G700, P-G500 and P-G300 cultures were co-infiltrated with P14 (lanes 3–8) or with P14 + UPF1DN (lanes 9–14). As a control for dominant-negative effect, PHA-m + PHA-s + P14 cultures were infiltrated or were co-infiltrated with UPF1DN (PHA-m + PHA-s + P14 + UPF1DN). These control samples were run on the same gel (lanes 1 and 2). RNA gel blot was hybridized with PHA-s probe. Samples and photos were taken at 3 d.p.i.