Figure 2.
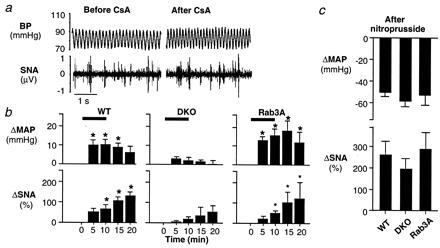
Attenuated effects of CsA on arterial BP and renal efferent SNA in synapsin I and II DKO mice. (a) Attenuated effect of CsA in a DKO mouse. CsA (10 mg/kg i.v.) had little or no effect on BP or renal efferent SNA in this synapsin-deficient mouse. (b) Effects of synapsin deficiency on responses to CsA. Changes in MAP and renal efferent SNA were recorded during and after CsA (10 mg/kg i.v.) in WT (n = 7), Rab3A KO (n = 5), and synapsin DKO (n = 15) mice. In both WT and Rab3A KO mice, MAP and renal efferent SNA increased significantly with CsA. These increases were greatly attenuated in the DKO mice. (c) Effect of synapsin deficiency on the sinoaortic baroreceptor reflexes. Baroreflex function was compared in WT (n = 5), DKO (n = 7), and Rab3A KO (n = 5) mice by measuring the peak reflex increase in renal efferent SNA evoked by decreasing MAP with nitroprusside (5–10 μg/kg i.v.). In synapsin DKO, comparable decreases in MAP to those produced in the two groups of control mice evoked comparable increases in renal efferent SNA, indicating a preserved baroreceptor reflex. Horizontal bars denote the period of CsA infusion. *, P < 0.05, compared with baseline (time 0).
