Figure 3.
nrp1-1 nrp2-1 Roots Show Defects in Cell Division, Viability, and Cellular Organization.
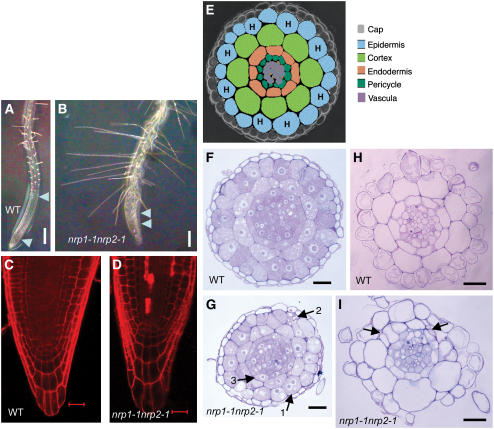
(A) and (B) Primary roots of 12-d-old seedlings of the wild type and the double mutant nrp1-1 nrp2-1, respectively. The region between two arrowheads indicates the elongation zone. Bars = 0.5 mm. (C) and (D) Longitudinal confocal sections of the wild-type and the double mutant nrp1-1 nrp2-1 roots of 7-d-old seedlings, respectively. Propidium iodide (red fluorescence) only stains the cell wall in living cells but stains the entire cell in dead cells. Dead cells were observed in 8/10 mutant but 0/10 wild-type primary root tips. Bars = 20 μm.
(E) Schema of transverse section of root apex with different colors indicating different cell types. H, root hair cell.
(F) and (G) Transverse sections within the root elongation zone of wild-type and double mutant nrp1-1 nrp2-1 10-d-old-seedlings, respectively. Arrows indicate different types of abnormal cells having either two nuclei (1) possibly due to a defect in cytokinesis, granular and shrunken form (2) because of death, or irregular size and misplacement in cell layers (3). Bars = 50 μm.
(H) and (I) Transverse sections within the differentiation zone of wild-type and the double mutant nrp1-1 nrp2-1 roots from 10-d-old-seedlings, respectively. Arrows indicate extra cell divisions. Note that the wild-type root contains the invariant eight cortical and endodermal cell files. Bars = 50 μm.