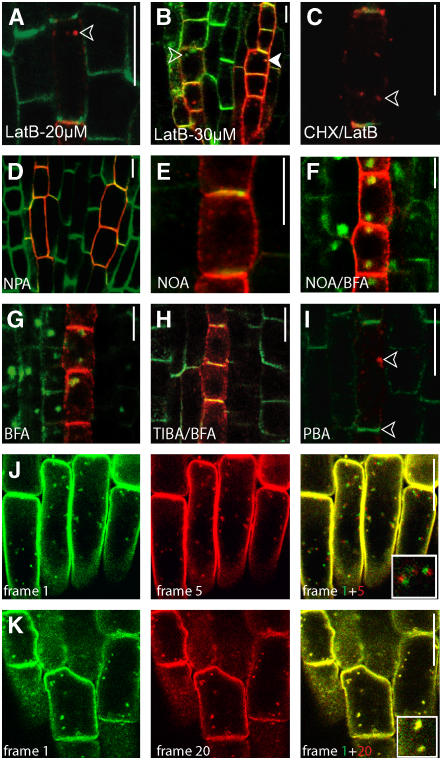
Figure 5.
Auxin and Auxin Transport Inhibitors: Effects on AUX1 Dynamics.
(A) The actin-depolymerizing agent Lat B preferentially targets AUX1 and causes AUX1 retrieval from the PM and its aggregation.
(B) At higher Lat B concentrations, PIN1 is also affected.
(C) AUX1 aggregation also occurs when protein synthesis is inhibited. CHX, cycloheximide.
(D) Naphthylphthalamic acid (NPA) affects the polar distribution of AUX1 and PIN1.
(E) 1-NOA does not affect the localization of AUX1 and PIN1.
(F) AUX1 and PIN1 readily accumulate in BFA compartments in the presence of 1-NOA.
(G) BFA treatment leads to AUX1/PIN1 accumulation in BFA compartments.
(H) TIBA inhibits the BFA-induced aggregation of AUX1/PIN1.
(I) PBA treatment causes the internalization and subcellular aggregation of AUX1 but not of PIN1 (indicated by the lower arrowhead).
(J) Subcellular dynamics of AUX1:YFP (yellow). Overlay of frame 1 (green) on frame 5 (+30 s; red).
(K) TIBA blocks the subcellular dynamics of AUX1:YFP. Overlay of frame 1 (green) on frame 20 (+120 s; red).
Open arrowheads indicate AUX1 accumulation, and the closed arrowhead shows AUX1/PIN1 colocalization. Immunocytochemistry of protophloem cells is shown in (A) to (I), and live-cell imaging of lateral root cap cells is shown in (J) and (K). The localization of AUX1:HA is shown in red, and that of PIN1 is shown in green in (A) to (I). Bars = 10 μm.