Figure 1.
Characterization of the Gln1-3∷Mu and Gln1-4∷Mu Insertion Events.
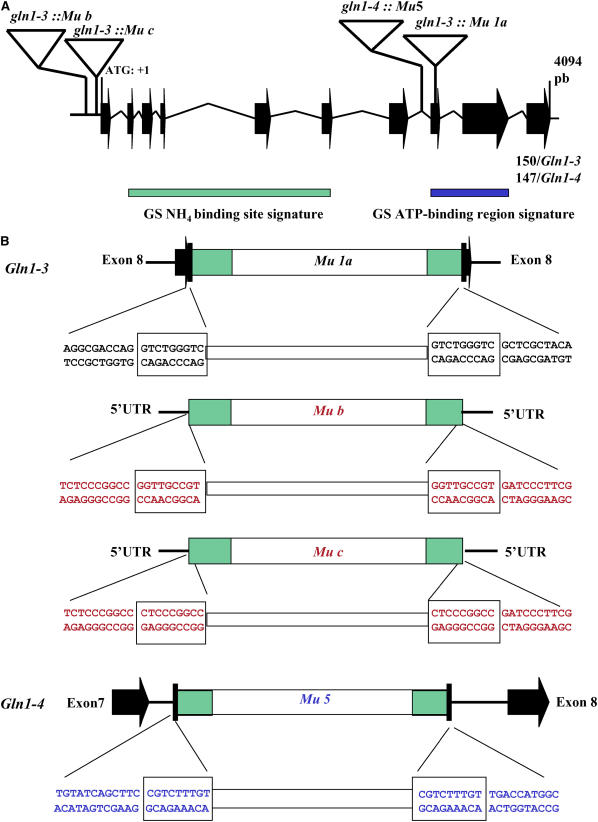
(A) Insertion position of the Mu elements within the Gln1-3 and Gln1-4 genes. For clarity and as the Gln1-3 and Gln1-4 genes show high sequence similarity, they are shown as a single structure. The Gln1-3 and Gln1-4 gene structure and exon sizes were determined by sequencing genomic DNA PCR products using primers designed from the corresponding cDNA sequences (Li et al., 1993): the Mu insertion sequences and the rice genomic clone AC105364. The rice and Gln1-3 and Gln1-4 genes consist of 10 exons (black arrows), ranging in size from 40 to 252 bp, and nine introns (black lines). The size of the last exon was 150 bp in Gln1-3 and 147 bp in Gln1-4. The intron and exon structure is drawn to scale. The gene numbering starts with the ATG codon (1 bp) and continues to the stop codon (position 3857 bp). The four Mu insertion events are indicated by triangles (not to scale). Also shown is the relative position of the GS-NH4+ binding site signature (green rectangle) and the GS-ATP binding region signature (blue rectangle).
(B) Sequence characterization of Mu insertions in Gln1-3 and Gln1-4. The nucleotide sequences flanking the 5′ and 3′ ends of the inserted transposons in Gln1-3∷Mu1 and Gln1-4∷Mu5, respectively, are presented and in each case show the Mu-specific 9-bp duplication of the target DNA (boxed). Sequence analysis of the flanking regions surrounding the Mu elements indicated that in the case of Gln1-3∷Mu1a, the insertion had occurred within exon 8, and in the case of Gln1-4∷Mu5, the insertion had occurred within the intron separating exon 7 and exon 8, while Gln1-3∷Mub and c are both located within the 5′-untranslated region. Black lettering indicates sequences derived from exons, and blue lettering indicates sequences derived from introns.