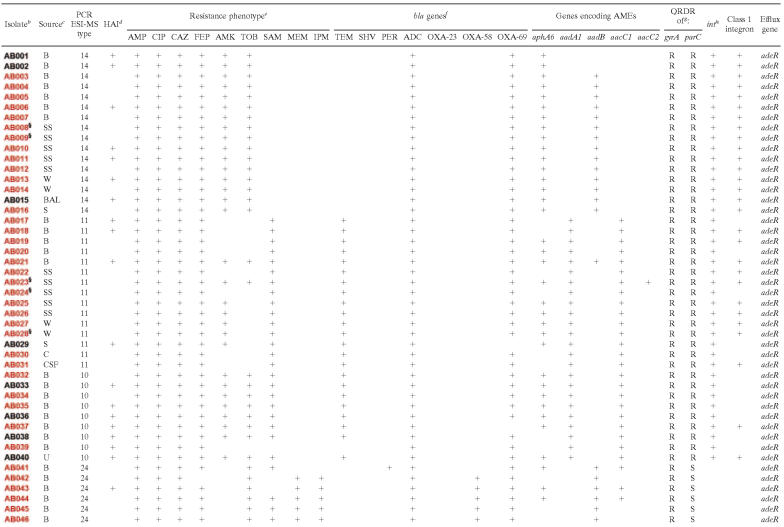
TABLE 6.
Summary of resistance: phenotypic and genetic characteristics of the isolatesa
+, presence of indicated gene or resistance phenotype.
All isolates are A. baumannii, except AG073 (Acinetobacter genome species 3) and AJ075 (Acinetobacter johnsonii). Red, deployed to Iraq/Kuwait; blue, deployed to Afghanistan; black, nondeployed; §, colonization (all others are clinically significant infections).
B, blood; SS, skin survey; W, wound; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; S, sputum; C, intravenous catheter; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; U, urine; TA, trachea aspirate.
HAI, hospital-acquired infection.
AMP, ampicillin; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CAZ, ceftazidime; FEP, cefepime; AMK, amikacin; TOB, tobramycin; SAM, ampicillin-sulbactam; MEM, meropenem; IPM, imipenem.
OXA-23, blaOXA-23-like gene; OXA-58, blaOXA-58-like gene; OXA-69, blaOXA-69-like gene; ADC, Acinetobacter-derived cephalosporinase.
Resistance (R) and susceptibility (S) were based on HinfI endonuclease restriction digests.
int, integrase genes intI1, intI2, and intI3.