Figure 3.
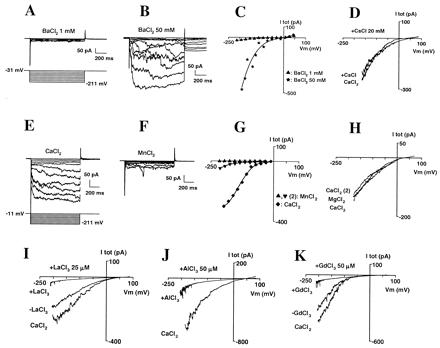
Selectivity and block of the inward Ca2+ current. (A–C) Whole-cell current sensitivity to increases in external BaCl2 concentration; successively 1 (A) and 50 (B) mM. (C) Corresponding I–V curve of total current. (D) Effect of the addition of CsCl (20 mM) on Ca2+ current. External CaCl2 was 10 mM; traces were obtained by hyperpolarizing the membrane to −200 mV during 1 s to activate the Ca2+ conductance, then slowly depolarizing (30 mV/s) up to +90 mV; each trace is the average of three successive repeats. Currents were plotted against corresponding voltages. (E–G) Comparison of whole-cell currents with external Ca2+ or Mn2+. Currents were recorded successively in 10 mM MnCl2 (traces not shown), CaCl2 (E), and, again, MnCl2 (F). (G) Corresponding I–V. (H) Comparison of whole-cell currents with external Ca2+ or Mg2+. Currents were recorded successively in 10 mM CaCl2, MgCl2, and, again, CaCl2; voltage-clamp protocol was similar to that in D. (I–K) Block of the Ca2+ current by La3+ (I; 25 μM), Al3+ (J; 50 μM), and Gd3+ (K; 50 μM). External CaCl2 was 10 mM; Voltage-clamp protocols were similar to D.
