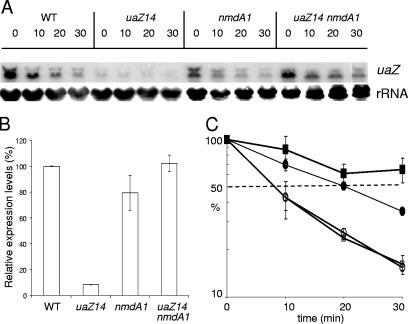
FIG. 4.
Analysis of uaZ transcript levels at 37°C. RNA was extracted from wild-type (WT), uaZ14, nmdA1, and uaZ14 nmdA1 strains after induction using uric acid as the sole nitrogen source for 2 h at 37°C. Transcription was inhibited for 10 min prior to commencement of the time course, and samples were taken over a 30-min period, as indicated. (A) uaZ levels were monitored by Northern analysis. (B) The relative levels of uaZ transcript in the four strains at time zero were determined using RT-PCR, which was used to monitor specifically the level of spliced mRNA. (C) RT-PCR was also used to monitor degradation rates. uaZ mRNA appears to be significantly more labile in the WT (uaZ+ nmdA+) (□) and uaZ+ nmdA1 (○) strains than in the uaZ14 nmdA+ (▪) and uaZ14 nmdA1 (•) strains. Quantitative analysis of the Northern data gave similar results (data not shown). Standard errors are indicated.