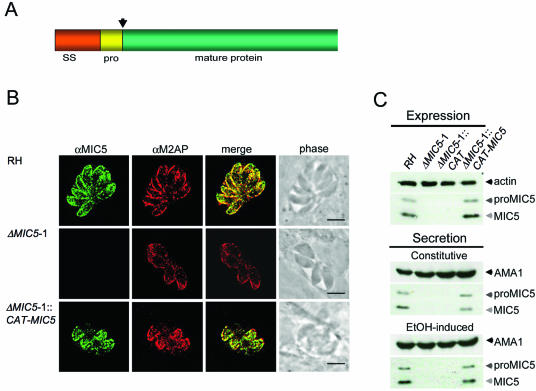
FIG. 1.
MIC5 ablation and complementation. (A) MIC5 protein schematic, showing the 29-amino-acid (aa) signal sequence (SS), the 14-aa propeptide (pro) (arrow denotes cleavage site), and the 138-aa mature sequence. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of intracellular parasites 24 h postinoculation. Monolayers were fully permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 and stained with anti-MIC5 and anti-M2AP. Signals colocalize at the apical ends of RH and ΔMIC5 complemented parasites (ΔMIC5-1::CAT-MIC5) arrayed outward in a rosette, whereas no MIC5-specific signal is observed in ΔMIC5-1. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Immunoblots of parasite lysates and constitutive and induced ESA fractions from RH, ΔMIC5-1, ΔMIC5-1::CAT, and ΔMIC5-1::CAT-MIC5.