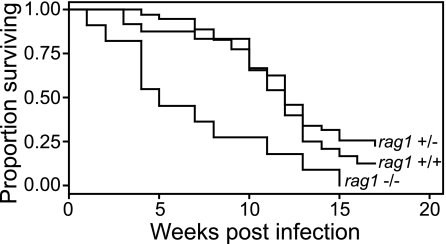
FIG. 3.
Zebrafish lacking rag1 are hypersusceptible to infection by M. marinum. Twelve rag1 wild-type, heterozygous, or mutant fish were infected with 8 CFU of WT bacteria and reared in separate tanks. Each tank was monitored for mortalities over a 16-week period. A Kaplan-Meier curve was calculated for each group of fish, and compared to rag1 WT or heterozygous fish, rag1 mutant animals showed a significant difference in survival as calculated by log-rank test (P = 0.002). The Cox proportional hazards model was used to quantify the differences between groups and confirmed significant differences in survival between mutant and wild-type fish (HR = 2.7; 95% CI = 1.6 to 4.7; P < 0.0001) and mutant and heterozygous fish (HR = 3.2; 95% CI = 2.1 to 4.8; P < 0.0001). There was no significant difference in survival between WT and heterozygous fish (HR = 0.86; 95% CI = 0.46 to 1.63; P = 0.654).