Abstract
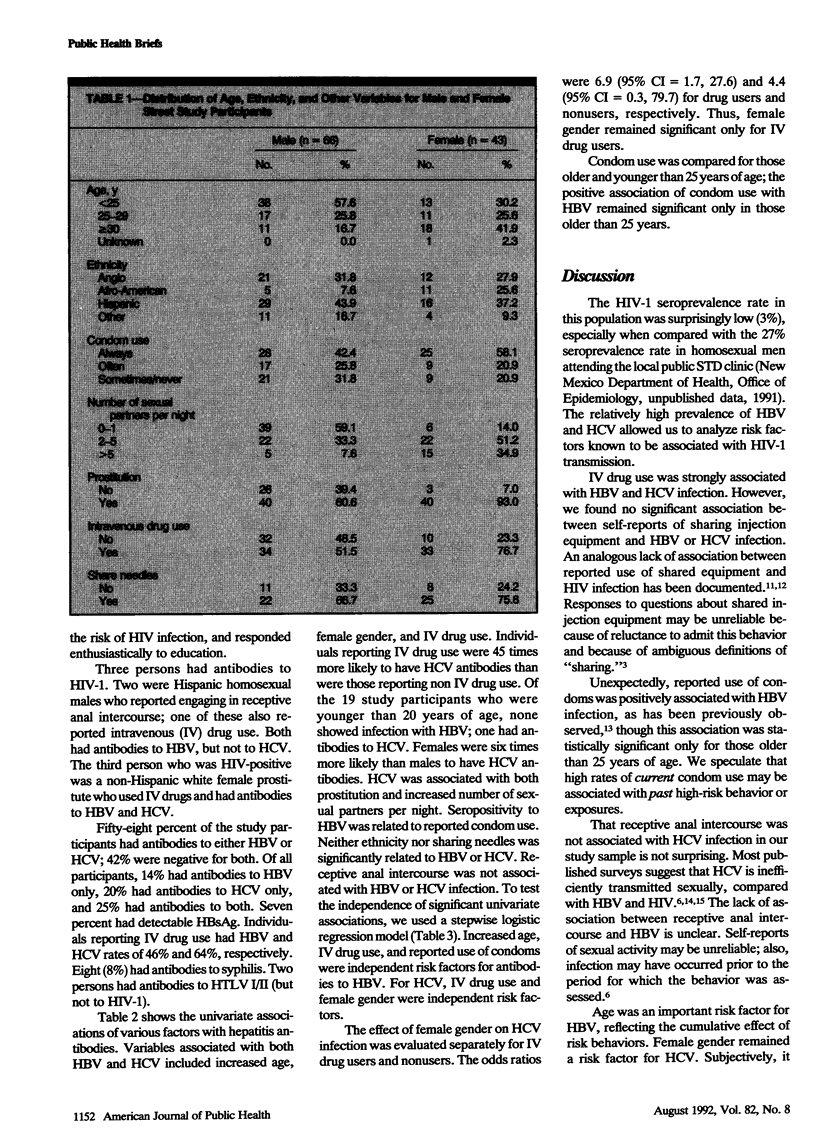
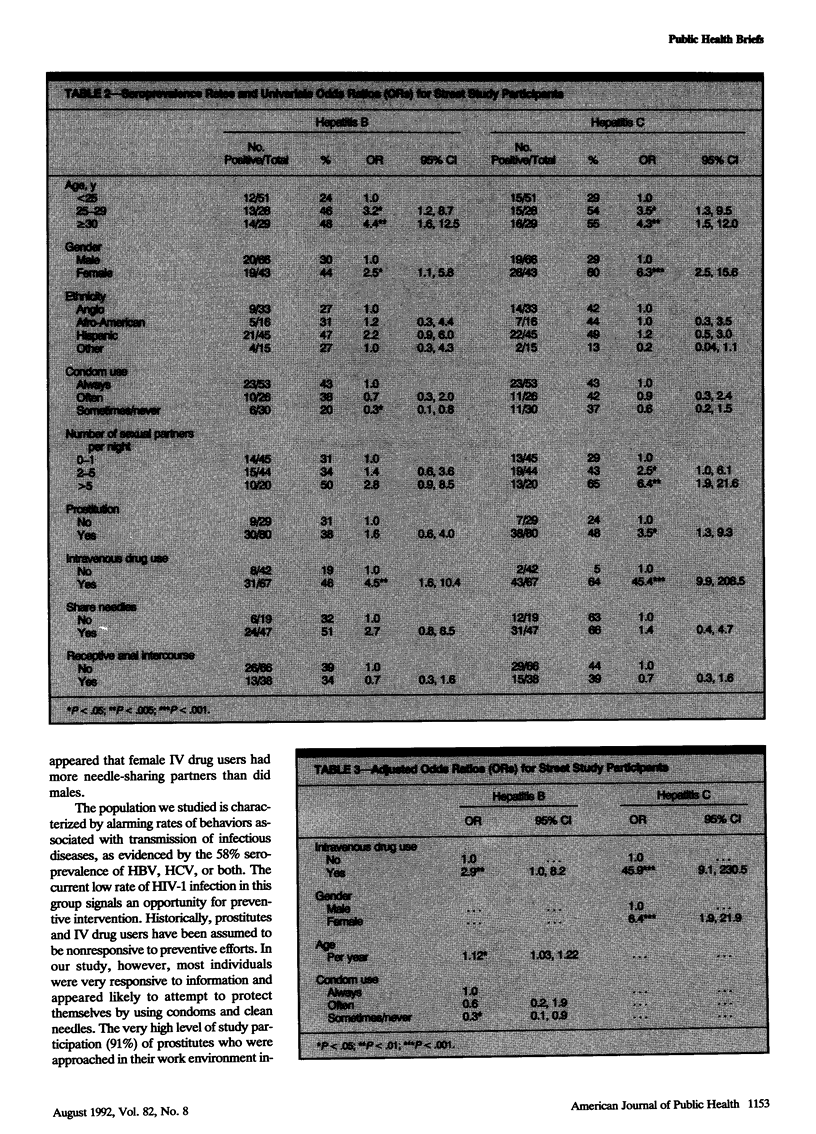
A survey of persons soliciting sex in an area known to be frequented by prostitutes in Albuquerque, NM, included 43 females and 66 males. Seroprevalence rates found in this population-based study were as follows: human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), 3%; hepatitis B, 39%; hepatitis C, 45%. Increased age, intravenous drug use, and condom use were independent risk factors for hepatitis B. Female gender and intravenous drug use were independent risk factors for hepatitis C. Neither sharing injection equipment nor engaging in receptive anal intercourse was independently associated with hepatitis B or C.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J., Batey R. G., Farrell G. C., Crewe E. B., Cunningham A. L., Byth K. Hepatitis C virus in intravenous drug users. Med J Aust. 1990 Sep 3;153(5):274–276. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1990.tb136900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban J. I., Esteban R., Viladomiu L., López-Talavera J. C., González A., Hernández J. M., Roget M., Vargas V., Genescà J., Buti M. Hepatitis C virus antibodies among risk groups in Spain. Lancet. 1989 Aug 5;2(8658):294–297. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90485-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyster M. E., Alter H. J., Aledort L. M., Quan S., Hatzakis A., Goedert J. J. Heterosexual co-transmission of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 15;115(10):764–768. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-10-764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams K. C., Escamilla J., Lozada Romero R., Macareno Alvarado E., Bonilla Giraldo N., Papadimos T. J., Rubio Martinez C., Garcia Gonzalez P. Hepatitis B infection in a non-drug abusing prostitute population in Mexico. Scand J Infect Dis. 1990;22(5):527–531. doi: 10.3109/00365549009027091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khabbaz R. F., Darrow W. W., Hartley T. M., Witte J., Cohen J. B., French J., Gill P. S., Potterat J., Sikes R. K., Reich R. Seroprevalence and risk factors for HTLV-I/II infection among female prostitutes in the United States. JAMA. 1990 Jan 5;263(1):60–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker J., Koblin B., Lewis B. F., Sullivan J. Demographic characteristics, risk behaviors, and HIV seroprevalence among intravenous drug users by site of contact: results from a community-wide HIV surveillance project. Am J Public Health. 1990 Sep;80(9):1062–1067. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.9.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. L. HIV seroprevalence among male IVDUs in Houston, Texas. Am J Public Health. 1990 Dec;80(12):1507–1509. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.12.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoek J. A., van Haastrecht H. J., Goudsmit J., de Wolf F., Coutinho R. A. Prevalence, incidence, and risk factors of hepatitis C virus infection among drug users in Amsterdam. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):823–826. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


