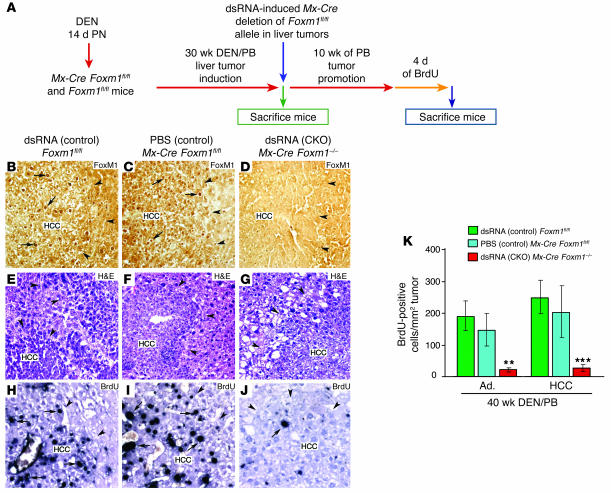
Figure 1. The mouse Foxm1 transcription factor is required for hepatic tumor progression.
(A) Diagram depicting experimental design of conditional deletion of Foxm1fl/fl in preexisting liver tumors. See Methods for details of DEN/PB treatment of mice to induce HCCs as described previously (8). To create the Foxm1 CKO, mice were injected with synthetic dsRNA to induce expression of the Mx-Cre recombinase transgene (Mx-Cre) to delete the mouse Foxm1fl/fl targeted allele at 30 weeks after DEN/PB treatment, and the mice were then subjected to 10 additional weeks of PB tumor promotion and were labeled with BrdU as described in Methods. Controls included dsRNA-treated Foxm1fl/fl mice and PBS-treated Mx-Cre Foxm1fl/fl mice. PN, postnatally. (B–D) dsRNA CKO Mx-Cre Foxm1–/– liver tumors display no detectable nuclear staining of Foxm1 protein as determined by immunostaining with Foxm1 antibody. (E–G) H&E staining of the indicated HCC liver sections after 40 weeks of DEN/PB exposure (tumor margins indicated by arrowheads). (H–J) BrdU incorporation was detected by immunostaining of liver tumor sections with monoclonal BrdU antibody from the indicated mice at 40 weeks following DEN/PB exposure. Arrows indicate nuclear staining for either Foxm1 protein or BrdU. (K) Graph of mean number of BrdU-positive cells per square millimeter liver tumor (±SD) as described in Methods. The asterisks indicate statistically significant changes: **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001. Ad., hepatic adenomas. Magnification: ×200 (B–G); ×400 (H–J).