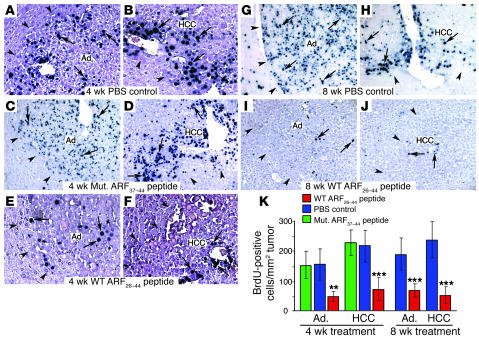
Figure 3. Treatment of mice with the WT ARF26–44 peptide diminishes proliferation of mouse hepatic tumors.
Hepatic tumors were induced in Foxm1fl/fl mice with DEN/PB treatment, and then they were treated with daily i.p. injections of 5 mg/kg body weight of WT ARF26–44 peptide or mutant ARF37–44 peptide or PBS for 4 or 8 weeks as described in the Figure 2A legend. These ARF peptide–treated mice were given drinking water with 1 mg/ml of BrdU for 4 days before sacrifice in order to obtain long-term labeling of the liver tumors (37). Arrows indicate nuclear staining for BrdU incorporation, and arrowheads show liver tumor margins. (A–J) BrdU incorporation was detected by immunohistochemical staining of liver tumor sections with monoclonal BrdU antibody from mice treated with the indicated ARF peptides. (K) Graph of mean number of BrdU-positive cells per square millimeter liver tumor (±SD) following treatment with WT ARF26–44 peptide or mutant ARF37–44 peptide or PBS. We calculated the mean number (±SD) of BrdU-positive hepatocyte nuclei per square millimeter liver tumor from 3 distinct mice treated with ARF peptide as described in Methods. The asterisks indicate statistically significant changes: **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001. Magnification: ×200 (A–J).