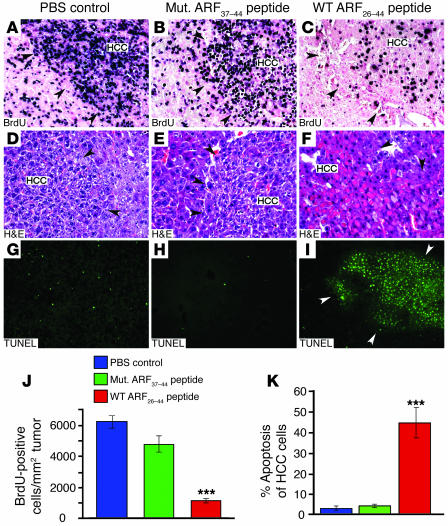
Figure 7. WT ARF26–44 peptide treatment reduces proliferation and increases apoptosis of HCCs, which were induced in Arf–/– Rosa26-FoxM1b Tg mice by DEN/PB.
Highly proliferative HCC tumors were induced in Arf–/– Rosa26-FoxM1b Tg mice following 33 weeks DEN/PB treatment. The Arf–/– Rosa26-FoxM1b Tg mice received daily i.p. injections of the WT ARF26–44 peptide (inhibitor of FoxM1 function) or mutant ARF37–44 peptide or PBS for 4 weeks. (A–C) Liver tumor sections were subjected to immunohistochemical staining with BrdU monoclonal antibody to determine HCC proliferation. Liver tumor sections were histologically stained with H&E (D and E) to identify red apoptotic cells or stained for apoptosis using the TUNEL assay (G–I). Black arrowheads indicate the boundaries of the HCC tumor, and white arrowheads (I) indicate the boundary of the HCC region. (J) We counted the BrdU-positive cells in HCCs and used this information to calculate the number of BrdU-positive cells per square millimeter liver tumor tissue (±SD). (K) We counted the TUNEL-positive cells in HCCs and used this information to calculate the percent HCC apoptosis (±SD). P values calculated by Student’s t test: ***P ≤ 0.001. Magnification: ×200 (A–F); ×100 (G–I).