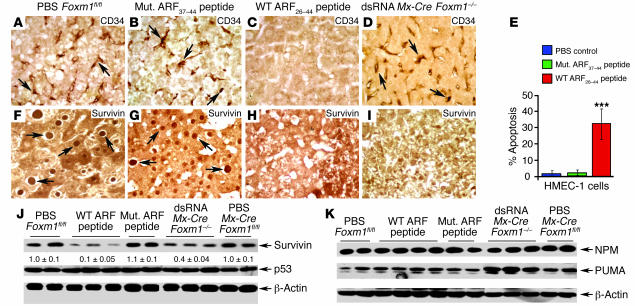
Figure 8. WT ARF26–44 peptide reduces angiogenesis and survivin expression in mouse HCC.
The CD34 protein is a marker for newly formed sinusoid-like capillaries in HCC regions (39–41), whereas survivin is critical in preventing apoptosis of tumor cells (45–48). Antibodies specific to either CD34 or survivin were used to immunostain HCC tumor sections from mice treated with mutant ARF37–44 peptide, WT ARF26–44 peptide, or PBS or from dsRNA CKO Mx-Cre Foxm1–/– mice. (A–D) Mice treated with WT ARF26–44 peptide display no CD34-positive endothelial cells in HCC capillaries, whereas CD34 staining (indicated by arrows) was abundant in endothelial cells of control mouse HCCs. (E) WT ARF26–44 peptide induces apoptosis of HMEC-1 cells. HMEC-1 cells were treated for 48 hours with 100 μM of WT ARF26–44 peptide or mutant ARF37–44 peptide or with PBS and then assayed for apoptosis as described in Methods. Shown graphically is the percent apoptosis of HMEC-1 cells in response to ARF peptide treatment. (F–I) Reduced survivin expression in WT ARF26–44 peptide–treated and Foxm1–/– liver tumors. Arrows indicate nuclear staining for survivin protein. (J) Western blot analysis reveals significant decrease in survivin protein expression in WT ARF26–44 peptide–treated mouse tumors. (K) No decrease in expression of NPM protein or p53-regulated proapoptotic PUMA protein is found in WT ARF26–44 peptide–treated mouse tumors. A slight increase in hepatic tumor levels of PUMA was found in mice treated with dsRNA. Magnification, ×400.