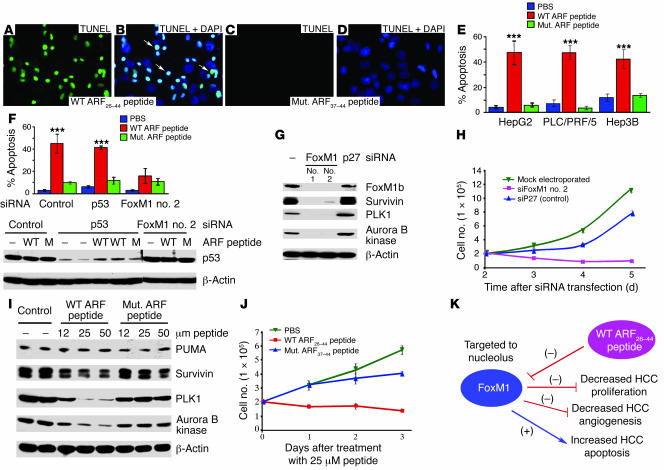
Figure 9. WT ARF26–44 peptide–induced apoptosis of human hepatoma cell lines.
Human hepatoma HepG2 (A–E), PLC/PRF/5 (expressing p53 mutant protein), or Hep3B (p53-deficient) cells were treated for 24 hours with 25 μM of WT ARF26–44 or mutant ARF37–44 peptide; they were then analyzed for apoptosis by TUNEL assay, and percent apoptosis (±SD) was calculated (E; ***P ≤ 0.001). Merged DAPI and TUNEL staining (A and C) images show TUNEL-positive nuclei of HepG2 cells (white arrows; B and D). (F) Graphic representation of WT ARF26–44 peptide–treated HepG2 cells showing that apoptosis is induced in p53-depleted cells but not in FoxM1-deficient cells. Western blot analysis is presented below the graph, showing effective downregulation of p53 protein levels following p53 siRNA electroporation and that treatment with WT ARF26–44 (WT) or mutant ARF37–44 peptide (M) does not alter p53 protein levels. (G and I) At 48 hours after electroporation with siFoxM1 no. 2 or p27 siRNA duplexes (G), or treatment with WT or mutant ARF peptide (I), HepG2 cells were analyzed for protein expression of survivin, PLK1, and aurora B kinase by Western blot analysis. We also determined a growth curve of HepG2 cells at the indicated days following siRNA transfection (H) or at the indicated days after ARF peptide treatment (J) as described in Methods. (K) Model summarizing findings in this article with WT ARF26–44 peptide. Magnification, ×400.