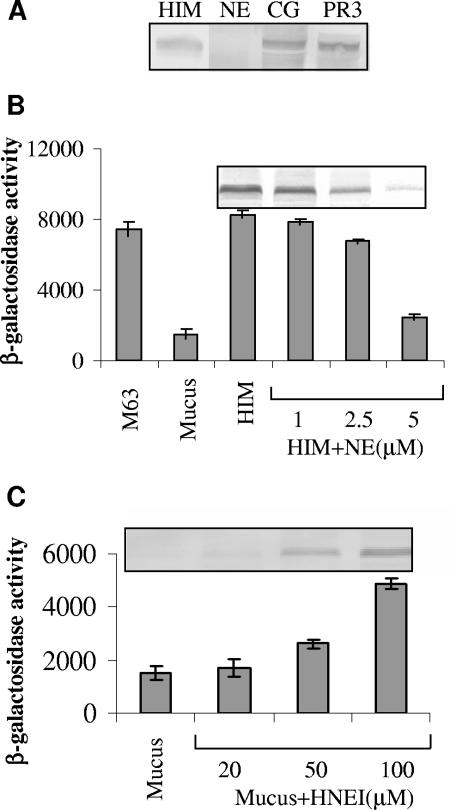
FIG. 2.
Effect of human neutrophil proteases on flagellin synthesis. (A) NE altered flagellin expression. P. aeruginosa PAK was incubated in heat-inactivated mucus (HIM) with or without NE, CG, and PR3 (5 μM) for 6 h. The reactions were processed for immunoblotting with flagellin-specific antibody. Similar numbers of bacteria were loaded, as ensured by measuring the CFU. (B) Human NE repressed fliC transcription. The activity of the fliC promoter was measured by growing the P. aeruginosa PAKfliC::lacZ reporter strain in M63, mucus, or heat-inactivated mucus (HIM) alone or in the presence of HIM supplemented with different concentrations of NE (1, 2.5, and 5 μM) for 6 h. The addition of 5 μM NE significantly (P < 0.0005) decreased fliC expression. Error bars indicate the means ± the SD. The values given were obtained from three independent experiments. The corresponding Western blots with flagellin-specific antibody are shown at the top of the graph. (C) The inhibition of NE activity by HNEI increased fliC expression. The reporter strain was incubated in mucus alone and in mucus containing different concentrations of HNEI (20, 50, and 100 μM) for 6 h. At 100 μM HNEI, a substantial increase in fliC expression was observed (P < 0.0005). Error bars indicate the means ± the SD. The corresponding immunoblot is shown at the top.