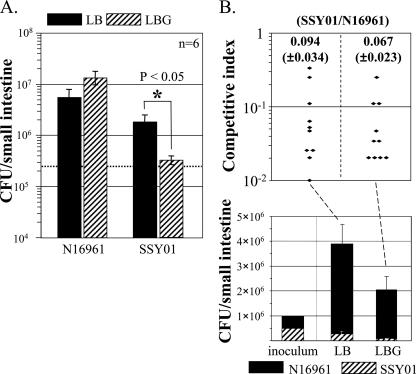
FIG. 6.
Effect of glucose on in vivo colonization of SSY01. (A) Infant mice were individually infected with 2.5 × 105 CFU (dashed line) of wild-type N16961 or SSY01. In 24 h, bacteria were recovered from mice and plated on appropriate media for enumeration. Prior to inoculation, bacterial cells, which were grown in LB to an OD600 of ∼0.5, were diluted 500-fold in fresh LB containing 0% (LB) or 2.5% (LBG) glucose. Six mice were used for each group, and means ± standard errors of the means are presented on a logarithmic scale. For SSY01, the decrease in CFU upon coinoculation with glucose was statistically significant (*, P < 0.05). (B) Infant mice were coinfected with 5 × 105 CFU of each strain. Again, bacterial cells were diluted in LB or LB containing 2.5% glucose before inoculation. After 24 h of incubation, CFU of each strain was enumerated and plotted in a linear scale. The competitive index represents the ratio of SSY01 to N16961 recovered after incubation. Ten mice were used for each infection, and means ± standard errors of the means are presented.