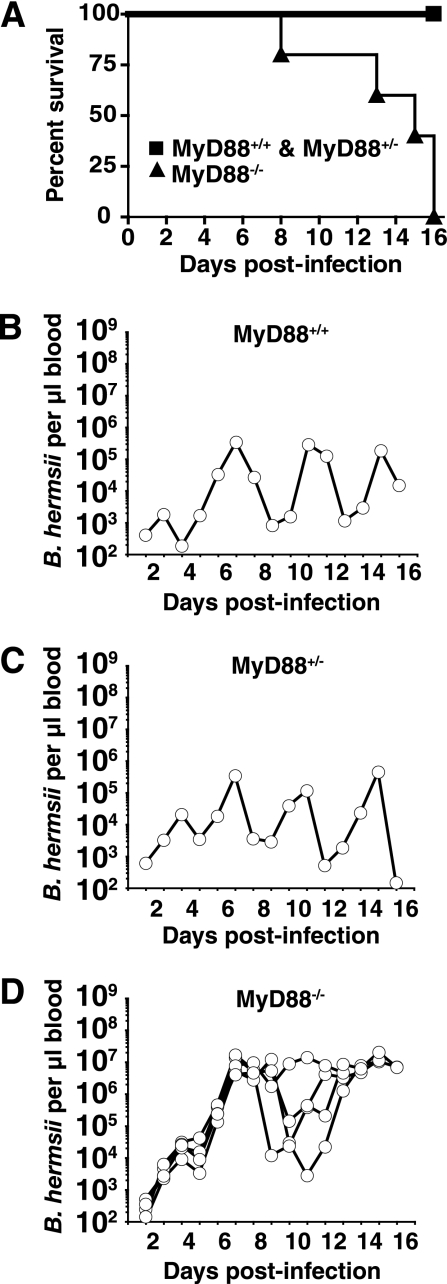
FIG. 1.
TLR signaling plays a crucial role in the control of B. hermsii levels in the blood. Mice were infected intraperitoneally with 1 × 106 B. hermsii cells (DAH isolate) and monitored daily for survival and bacterial levels in blood. DNA was isolated from 10 μl of blood, and B. hermsii levels were determined by quantitative PCR as described in Materials and Methods. Numbers reflect copies of the B. hermsii gene glpT normalized to the volume of blood. Kaplan-Meier survival plot of MyD88+/+, MyD88+/−, and MyD88−/− mice infected with B. hermsii (A) displaying significantly greater survival in MyD88+/+ and MyD88+/− mice than MyD88−/− mice infected with B. hermsii (P < 0.5). Also shown are B. hermsii levels in blood of one MyD88+/+ mouse, representative of three mice (B), B. hermsii levels in blood of one MyD88+/− mouse, representative of four mice (C), and B. hermsii levels in blood of five MyD88−/− mice (D).