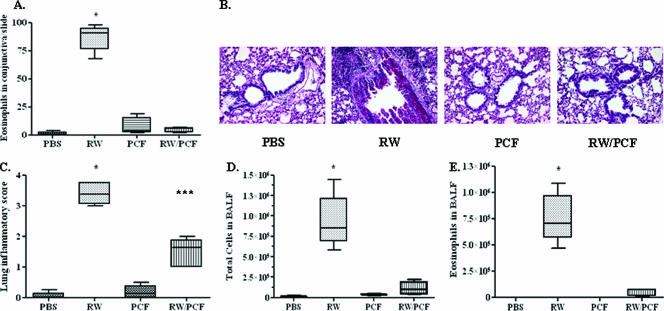
FIG. 1.
Allergic conjunctival and pulmonary inflammation following RW sensitization and challenge. Five to eight A/J mice per treatment group were treated with PBS, PCF, RW, or RW and PCF. A. RW challenge in sensitized animals resulted in a significant infiltration of eosinophils into the conjunctiva (***, P < 0.001) compared with all other treatment groups). This allergen-induced eosinophil infiltration was reduced by PCF administration during RW sensitization (RW/PCF). B. Periodic acid-Schiff staining of representative lung tissue sections 72 h after allergen challenge. C. Lung sections were assigned an inflammatory lung score using a scale of 0 to 4, with 4 representing the score for a maximal inflammatory response in the lung. Mice given RW sensitization had a significant increase in lung inflammatory scores compared to those of mice sensitized with PBS or PCF treatment alone post-RW challenge (***, P < 0.001). Mice treated with PCF during RW sensitization had reduced lung inflammatory scores after RW challenge compared to animals given RW alone. D. Total cell numbers were counted from the BALF and demonstrated a significant increase in total cell numbers in the lung lumen in mice given RW sensitization (***, P < 0.001) compared with all other groups of mice. Mice treated with PCF during RW sensitization had significantly reduced cell numbers in the lung lumen after RW compared with animals given RW alone. E. Eosinophils were counted from the BALF as a measure of allergic inflammation. Mice given RW sensitization demonstrated a significant increase in eosinophil infiltrates in the BALF post-RW challenge (***, P < 0.001) compared to all other treatment groups. Mice treated with PCF during RW sensitization had significantly reduced eosinophil numbers in the BALF after RW challenge compared with animals given RW alone.