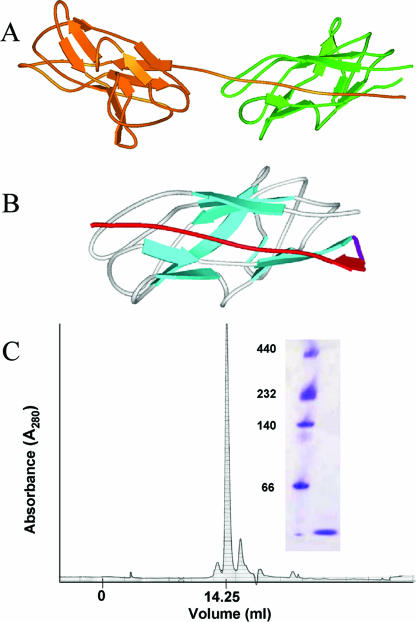
FIG. 1.
Design and creation of a folded monomeric Caf1 protein. (A) Ribbon diagram of Caf1 dimer (taken from PDB file 1P5U [40]) illustrating the donor strand complementation critical for correct folding of Caf1 polymer. (B) Energy minimized model of cpCaf1 structure based on 1P5U showing the engineered flexible linker (magenta) and repositioned N-terminal strand (red). (C) Schematic representation of rCaf1 and its mutant derivatives. Amino acid residue numbering of the mature protein is used in the numbering scheme, and as in panel B the engineered flexible linker is shown in magenta and repositioned N-terminal strand in red. (D) Superose 12 size exclusion chromatography of cpCaf1 (50 mM phosphate buffer [pH 7.4]) produced a single peak corresponding to the expected monomer size. CpCaF1 (16.1 kDa) elutes at a volume of 14.25 ml compared to carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa, 13.75 ml) and bovine serum albumin (66 kDa; 12.25 ml). Native polymeric Caf1 elutes in the void volume 6 ml (21). The inset shows Coomassie blue-stained native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons); lane 2, purified cpCaf1.