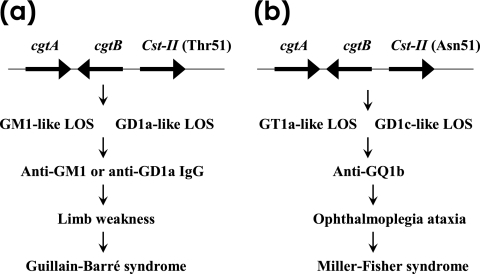
FIG. 3.
C. jejuni gene polymorphism as a determinant of clinical neuropathies after infection by the bacterium. (a) C. jejuni strains carrying cstII (Thr51) can express GM1-like or GD1a-like LOS on their cell surfaces. Infection by such C. jejuni strains can induce anti-GM1 or anti-GD1a IgG production in certain patients. Anti-GM1 or anti-GD1a IgG antibodies bind to GM1 or GD1a, respectively; these are expressed on motor nerves in the limbs and induce weakness. This binding induces the development of GBS. (b) In contrast, C. jejuni strains carrying cstII (Asn51) can express GT1a-like or GD1c-like LOS on their cell surfaces. Patients infected with C. jejuni (Asn51) more often were positive for anti-GQ1b IgG and had opthalmoplagia and ataxia (45). Anti-GQ1b IgG antibody binds to GQ1b, which is expressed on the oculomotor nerves and primary sensory neurons. This induces the development of Miller-Fisher syndrome (adopted from reference 106 with permission of the publisher).