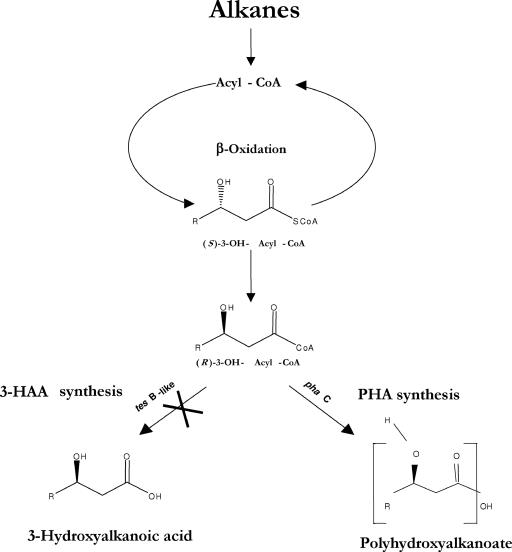
FIG. 6.
Suggested pathway of PHA biosynthesis in A. borkumensis SK2 and mutant strain C9 grown on hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are degraded via terminal oxidation to produce free fatty acids, which are then activated by an acyl-CoA synthase and subjected to β-oxidation. The (S)-3-OH-acyl-CoAs produced by β-oxidation are isomerized into (R)-3-OH-acyl-CoAs by the action of an isomerase. (R)-3-OH-Acyl-CoAs produced during β-oxidation are converted to either 3-HAA through the action of TesB-like acyl-CoA thioesterase or PHA through the action of PhaC synthase. The mutation in the TesB-like acyl-CoA thioesterase abolishes the production of free 3-HAA and channels (R)-3-OH-acyl-CoAs exclusively into PHA synthesis.