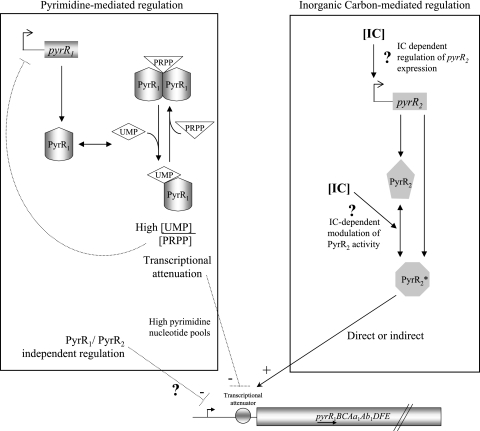
FIG. 5.
Model for PyrR1 and PyrR2 regulation of L. plantarum pyr regulon in response to pyrimidine availability and inorganic carbon. The regulated pyr genes studied include the pyrR1BCAa1Ab1DFE operon and pyrP. The gray circle schematizes pyr gene cis transcription regulatory elements that are involved in response to pyrimidine availability and IC at the DNA or the mRNA level. The activity of the RNA-binding PyrR1 protein is regulated by binding to antagonist effectors such as 5-phospho-d-ribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) and UMP. The UMP-PyrR1 complex binds to an attenuation site of the pyr mRNA, leading to terminated transcription (19). Another unknown mechanism independent of PyrR1 and PyrR2 activity operates under conditions of elevated intracellular pyrimidine nucleotide levels. IC regulation may occur at the level of pyrR2 expression or the gene product activity. PyrR2* represents the functional PyrR2 regulator.