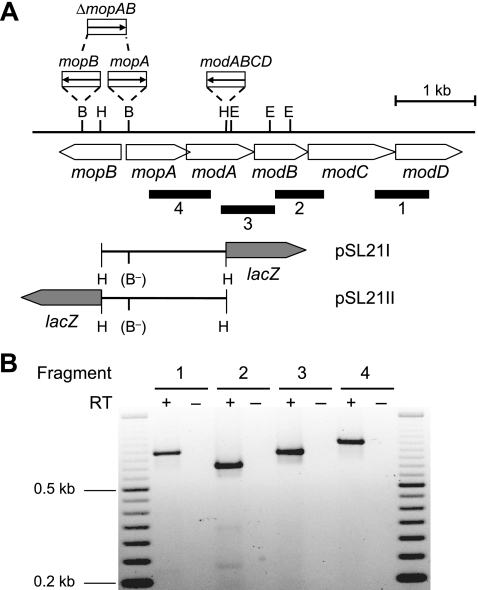
FIG. 1.
Transcriptional analysis of the R. capsulatus mopA- modABCD gene region. (A) Physical and genetic maps of the mop-mod gene region. The physical map is given for BamHI, EcoRI, and HindIII (B, E, and H, respectively). Black bars below the genetic map indicate DNA fragments 1 to 4 emerging from RT-PCR (see Materials and Methods and panel B). The corresponding primer pairs used for RT-PCR are listed in Table 2. Mutant strains defective for either mopA (R423AI), mopB (R423BI), mopA and mopB (R423CI), or modABCD (R438II) contain gentamicin resistance cassettes, with the directions of transcription of the Gm resistance gene symbolized by arrows. Hybrid plasmids pSL21I and pSL21II, carrying transcriptional modA-lacZ and mopB-lacZ fusions, respectively, are based on the mobilizable broad-host-range plasmid pML5. In these reporter plasmids, the BamHI sites were destroyed (indicated by B−) by cutting with BamHI, filling in protruding ends, and blunt-end religation, leading to a frameshift within the mopA coding region. Neither the Gm cassette nor the lacZ gene is drawn to scale. (B) Transcriptional analysis of the mopA-modABCD operon by RT-PCR. Total RNA was isolated from R. capsulatus cells grown under Mo-limiting conditions. Either RNA samples were treated with reverse transcriptase to synthesize cDNA (+) or, as a negative control, reverse transcriptase was omitted (−). A 50-bp DNA ladder (Fermentas, St. Leon-Rot, Germany) was used as a length standard.