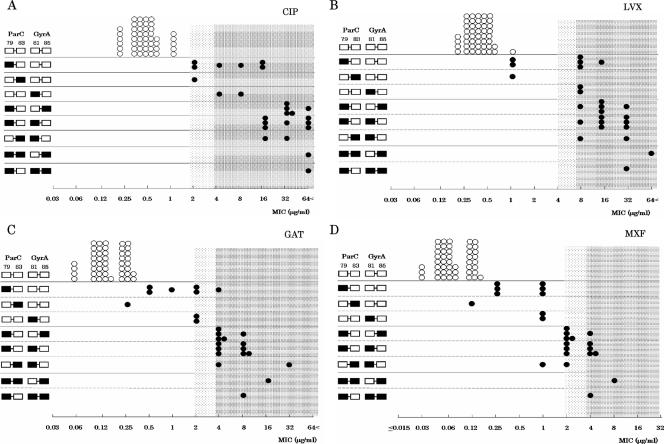
FIG. 2.
Comparison of outcomes between conventional FQ susceptibility testing and the PCR-MCA assay for genotyping QRDR mutants. Panels A, B, C, and D show results with CIP, LVX, GAT, and MXF, respectively. White squares represent the wild type, and black squares represent the mutant types for four positions of the QRDRs in the parC gene and gyrA gene obtained by the PCR-MCA assay. White circles represent wild-type strains, and black circles represent mutation-containing strains. The horizontal axis represents the MIC of each strain. The dark mesh area represents resistance, and the light mesh area represents intermediate susceptibility to each FQ. The CLSI MIC breakpoints (26) were used for the following drugs: LVX (susceptible, ≤2 μg/ml; intermediate, 4 μg/ml; and resistant, ≥8 μg/ml), GAT (susceptible, ≤1 μg/ml; intermediate, 2 μg/ml; and resistant, ≥4 μg/ml), and MXF (susceptible, ≤1 μg/ml; intermediate, 2 μg/ml; and resistant, ≥4 μg/ml). The breakpoint standard for CIP was obtained from the interpretive guideline supplied by the Japanese Society of Chemotherapy (susceptible, ≤1 μg/ml; intermediate, 2 μg/ml; and resistant, ≥4 μg/ml).