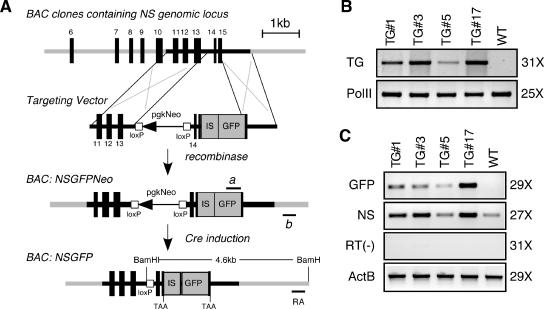
FIG. 4.
Creation of NS-overexpressing mice. (A) An NS gain-of-function mouse model was made by a BAC transgenic approach. An IRES-GFP cassette was engineered after the stop codon of NS. The targeting vector contained a LoxP-flanked pgk-neomycin cassette (pgkNeo), a partial 3′ sequence of NS before the stop codon, an IRES sequence, and a GFP reporter gene, sandwiched by two recombineering arms. The pgkNeo cassette was excised from the recombined BAC clone (BAC: NSGFPNeo), leaving a LoxP site in the nonconserved region of the 13th intron. All genomic sequences were preserved in the final transgene construct (BAC: NSGFP), including 150 kb upstream and 68 kb downstream of the NS locus. Lines a and b indicate primers used for genotype analyses. The transgenic allele will generate a 4.6-kb fragment in BamHI-digested Southern blots hybridized with the right-arm probe (RA). (B) Four transgenic lines with different levels of transgene dosage were detected by PCRs (TG). RNA polymerase II (PolII) PCRs were used as controls for the genomic DNA preparations. (C) The mRNA expression levels of the GFP and NS in the adult testis were measured by semiquantitative RT-PCRs. RT-minus [RT(−)] and β-actin (ActB) reactions were used as negative and positive controls. Amplification cycle numbers for panels B and C are indicated on the right.