Figure 2. .
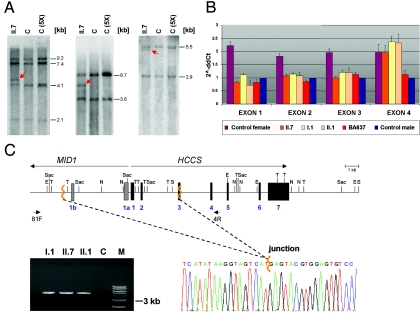
A submicroscopic deletion encompassing part of the HCCS gene is present in three members of the family of patient II.7. A, Southern blot hybridized with a probe covering the HCCS 5′ UTR and coding region. Genomic DNA samples of patient II.7 and controls were digested with SpeI and EcoRV (left), NdeI and SacI (middle), and TaqI (right). C = female control; C (5X) = human cell line with five X chromosomes. Various fragments of altered sizes (red arrows) were observed in II.7. B, Relative quantification of copy numbers of HCCS exons 1–4, by real-time PCR on genomic DNA of individuals I.1, II.1, and II.7. BA637 has MLS and displays monosomy of the Xp22 region.5 Values of HCCS exons 1–3 in II.7, II.1, and I.1 are comparable to that of a haploid sample. C, Schematic representation of part of the MLS critical region (top). MID1 and HCCS genes are indicated by long arrows, and primers used for junction fragment amplification are indicated by short arrows. Exons 1a and 1b of MID1 are represented by bars, exons of HCCS by black boxes. Jagged orange lines indicate deletion breakpoints. E = EcoRV; N = NdeI; S = SpeI; Sac = SacI; T = TaqI. Bottom left panel, Amplification of a junction fragment from genomic DNA of I.1, II.1, and II.7 but not from a control (C). M = DNA marker. Bottom right panel, Part of the DNA sequence electropherogram of the rearrangement-specific junction fragment. The deletion breakpoint is indicated by a jagged orange line. The 8.6-kb deletion encompasses HCCS exons 1–2, part of exon 3, and exons 1a and 1b of MID1.