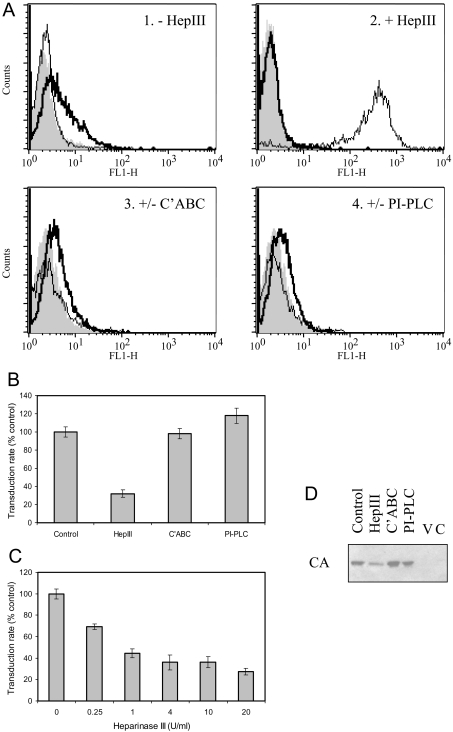
Figure 3. Effect of enzymatic digestion of GAGs.
(A) TE671 cells were analysed by FACS for cell-surface HS, without/with digestion for 1 h at 37 °C with 10 units/ml heparinase III (panels 1 and 2: ‘−HepIII’ and ‘+HepIII’ respectively), using monoclonal antibodies 10E4 (thick line) or 3G10 (thin line); data are overlaid on those resulting from use of the secondary antibody alone (solid grey profile). 10E4 staining for HS was eradicated by heparinase III (HepIII) digestion, while 3G10 staining for the neo-epitope generated upon digestion was dependent on such treatment. Similarly, detection of CS (panel 3: ‘+/−C'ABC’) in control cells (thick line) was eradicated by treatment with 10 units/ml chondroitinase ABC for 1 h at 37 °C (thin line), and detection of CD55 (panel 4: ‘+/−PI-PLC’) in control cells (thick line) was eradicated by treatment with 4 units/ml PI-PLC for 1 h at 30 °C (thin line). Enzyme treatment was specific for the appropriate target; additionally, 4-fold serial dilutions of the amount of enzyme used indicated that CS removal was equally effective at 0.6 unit/ml C'ABC, whereas residual HS and CD55 were detected following digestion with 2.5 units/ml heparinase III and 1 unit/ml PI-PLC respectively (results not shown). (B) Transduction rate assay of the effect of incubating virus for 4 h at 37 °C without enzyme (control) or with 4 units/ml heparinase III or chondroitinase ABC (C'ABC), or for 4 h at 30 °C with 4 units/ml PI-PLC. Treatment with heparinase III resulted in significant reduction (P<0.01, one-way ANOVA compared with control), whereas C'ABC and PI-PLC were ineffective (P>0.05). Results shown are means±S.E.M. values (n=3). (C) The effect on the transduction rate of treating virus with heparinase III was dose-dependent on enzyme concentration. All concentrations resulted in significant inhibition (P<0.01, one-way ANOVA compared with control), but there was no additional benefit for use of concentrations above 1 unit/ml (P>0.05). Results shown are means±S.E.M. values (n=3). (D) Determination of cell-associated viral CA by Western blotting was used as a direct assay of the effect of enzyme treatment of virus as in (B) on subsequent binding. Negative controls for the binding assay were virus alone (V) and cells without virus exposure (C).