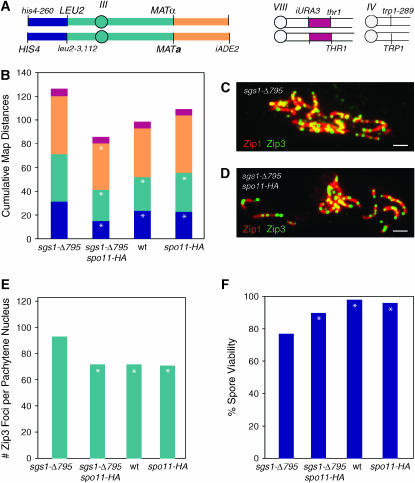
Figure 3.—
SPO11-HA suppresses sgs1-Δ795. (A) Configuration of markers in strains used for analysis of crossing over in various mutant backgrounds. (B) COs were measured in four intervals in wild type (BR4316), sgs1-Δ795 (BR4474), spo11-HA (BR4357), and sgs1-Δ795 spo11-HA (BR4475). Intervals are designated by the color utilized in A. Asterisks denote intervals in which map distances are significantly different from those in sgs1 (P < 0.05). (C) Spread nucleus from sgs1-Δ795 cell at pachytene stained for Zip3-GFP (green) and Zip1 (red) in pachytene. Yellow indicates regions of overlap. Bar, 1 μm. (D) Spread nucleus from sgs1-Δ795 spo11-HA stained as in C. Bar, 1 μm. (E) Zip3-GFP foci were quantified in pachytene-staged chromosome spreads. Asterisks denote strains in which the number of Zip3 foci is significantly different from that of sgs1-Δ795 (P < 0.05 using the t-test). (F) Spore viability. Differences between strains were assessed using the big G-test with spore viability patterns (i.e., four-, three-, two-, one-, and zero-spore viable, not shown). Asterisks denote strains in which spore viability is significantly different from that of sgs1-Δ795.