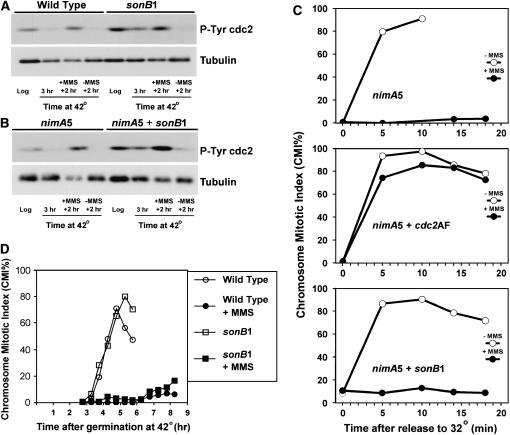
Figure 3.—
sonB1 mutants undergo tyrosine phosphorylation of Cdc2 and arrest in G2 in response to DNA damage. (A and B) Log-phase wild-type (GR5), sonB1 (CDS40), nimA5 (SO6), and nimA5 sonB1 (CDS119) cultures were shifted to 42° for 3 hr. Cultures were then divided into two and grown for another 2 hr in the presence or absence of 0.04% MMS. The relative levels of tyrosine 15-phosphorylated Cdc2 were determined by immunoblotting with an antibody specific for this epitope at the indicated time points. Levels of tubulin are shown as a loading control. (C) Chromosome mitotic index (CMI) of nimA5 (SO54), nimA5 cdc2AF (AT27), and nimA5 sonB1 (CDS119) germlings treated or not with 0.025% MMS during a nimA5 G2 arrest (42°) prior to release to nimA5 permissive temperature (32°) in the absence of MMS. Note that nimA5 and nimA5 + sonB1 cells did not display an increase in CMI percentage even 30 min following release from nimA5 arrest in the presence of MMS. (D) Wild-type (GR5) and sonB1 (CDS40) conidiospores were germinated in the presence or absence of 0.01% MMS and the CMI was determined by DAPI staining. Nocodazole (5 μg/ml) was included to prevent mitotic exit once cells entered mitosis.