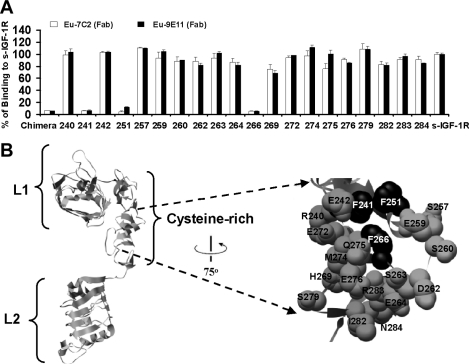
Figure 3. Epitope mapping using IGF-1R alanine mutants and the chimaeric IGF-1R/IR256–266 receptor.
(A) Alanine mutants, the chimaeric IGF-1R/IR256–266 receptor and wild-type IGF-1R (s-IGF-1R) were expressed as soluble receptors in culture medium. Levels of receptor in all supernatants were measured by ELISA and adjusted to 0.28 mg/ml prior to performing binding assays using europium-labelled mAbs 7C2 and 9E11 (Fab domains). Binding to culture supernatants is expressed as a percentage of binding to s-IGF-1R. Residue number is indicated below for alanine mutants. Chimaeric refers to the chimaeric IGF-1R/IR256–266. The graph shown is representative of three experiments and bars are means±S.D. of triplicates. (B) Ribbon diagram of the IGF-1R L1, CR and L2 domains based on the structure reported by Garrett et al [9] highlighted space-filled using black alanine mutants, which disrupt binding of europium-labelled 7C2 and 9E11 binding (residues Phe241, Phe251 and Phe266). The Figure was created using the UCSF Chimera molecular graphics program [45].