Figure 3. .
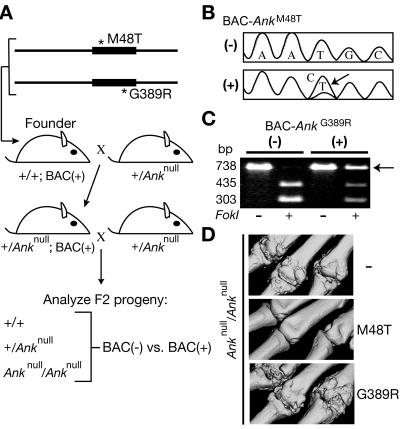
Transgenic expression of Ank disease alleles in mice. A, Breeding strategy. BACs were modified by homologous recombination in bacteria and were used to generate transgenic founders. Founders were crossed for 2 generations with +/Anknull mice. B–C, Analysis of RT-PCR products from +/Anknull;BAC+ and control +/Anknull;BAC− mice. In panel B, direct sequencing confirmed the expression of the AnkM48T allele, which is derived from a T→C bp change (arrow). In panel C, restriction digests confirmed the expression of the AnkG389R allele (arrow), which does not contain an FokI site. The wild-type allele was detected in all cases. D, μCT-derived volumetric reconstructions of digits 2–4 of the right forepaw at age 6 wk. Whereas the AnkM48T allele rescued the Ank null phenotype in two of three transgenic lines, the AnkG389R allele did not rescue in any of the four lines. As a control, the wild-type ANK protein expressed from an unmodified BAC rescued the Ank mutant phenotypes in four of four transgenic lines3 (and data not shown).