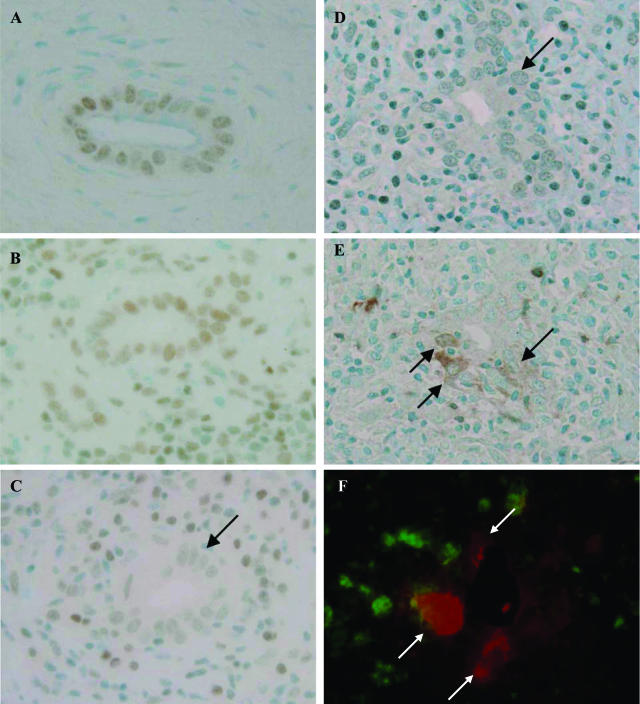
Figure 1.
Decreased expression of bmi1 and its relation with p16INK4a expression in BECs at the site of chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis in PBC. A and B: bmi1 was expressed in the nuclei of BECs in normal livers (A) and CVH livers (B). C: The expression of bmi1 was decreased (arrows) in BECs at the site of chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis. PBC, stage 2. D and E: Correlated expression of bmi1 (D) and p16INK4a (E) as a senescence-associated marker. The expression of bmi1 was decreased in BECs in the small bile ducts involved in chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis (D, arrow), and the expression of p16INK4a was increased in BECs in the same damaged small bile duct (E, arrow). PBC, stage 2. Immunostaining for bmi1 (A–D) and p16INK4a (E). F: Dual immunostaining of bmi1 (green fluorescence) and p16INK4a (red fluorescence) demonstrated the absence of bmi1 expression in nuclei of BECs expressing p16INK4a (arrows). Original magnifications, ×400.