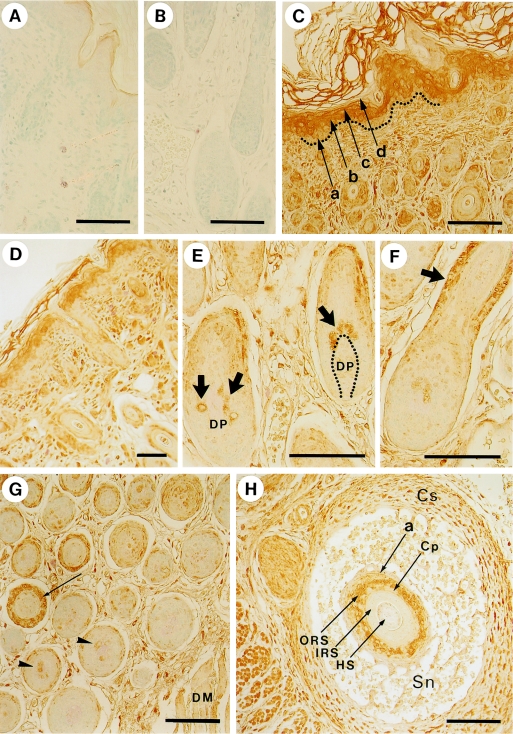
Fig. 3.
Localization of myosin in the skin and hair follicles detected by an anti-non-muscle myosin antibody. A, B) Control experiments in which the primary antibody was replaced by 1% bovine serum albumin. Samples were obtained from dorsal skin. C) Dorsal skin. In the epidermis of dorsal skin, a, b, c, and d represent the basal, spinous, granular, and innermost cornified layer, respectively. Dotted line indicates the basement membrane. D) Face skin. E) Hair bulbs in dorsal skin. The arrows show positive hair matrix cells adjacent to the dermal papilla (DP). F) Hair follicle in dorsal skin. The arrow denotes the positive staining of the outer root sheath. G) Middle (left side) and inner (right side) areas of dermis in dorsal skin. Each cross section of hair follicle in the middle area has a ring of positive staining in the outer root sheath (arrow), whereas that in inner area, which is adjacent to the dermal muscle (DM), is negative. Some of the hair matrix cells are stained (arrowheads). H) An oblique section of vibrissal follicle. Cs, capsule; Sn, sinus; a, border between epidermis and dermis, equivalent to the basement membrane; ORS, outer root sheath; Cp, companion layer; IRS, inner root sheath; HS, hair shaft. Bars=100 µm.