Figure 1.
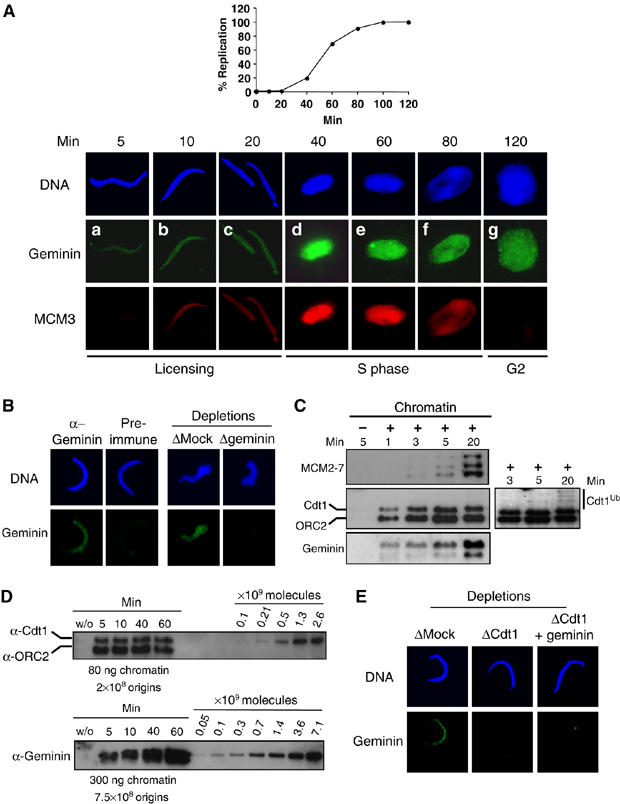
A fraction of geminin assembles in a Cdt1-dependent manner during licensing onto chromatin. (A) Upper panel: kinetics of the replication reaction performed as described in Materials and methods and expressed as the percentage of replicated sperm DNA compared to the total input DNA. Lower panel: sperm chromatin incubated in egg extract for indicated times and further detergent extracted and processed for immunofluorescence. Geminin was visualized by FITC (green) and MCM3 by Texas red (red). DNA was stained with Hoechst and is shown in blue. (B) Left panel: immunofluorescence of chromatin purified as in (A) after 5 min incubation in egg extract and stained either with geminin antibody or with preimmune serum. Right panel: immunofluorescence of chromatin after 5 min incubation in egg extract that was either Mock- or geminin-depleted. (C) Western blot analysis of Cdt1, MCM2–7, geminin and ORC2 (as a loading control) on chromatin purified after the indicated time. Also shown is a Mock purification (first lane), without added sperm chromatin, to determine background staining by non-chromatin bound proteins. A longer exposure of the Cdt1 blot is also presented to show polyubiquitination of Cdt1 at the onset of S phase. (D) Western blot analysis of purified chromatin following the indicated times of incubation in egg extract (S-phase entry at 40 min). A dilution series of recombinant Cdt1 and geminin was loaded on the same gel. The amount of loaded chromatin is indicated, as well as the corresponding number of origins (Lemaitre et al, 2005). (E) Geminin signal on chromatin incubated 5 min in egg extract, either Mock-depleted, Cdt1-depleted, or Cdt1-depleted and complemented with geminin before addition of sperm chromatin.
