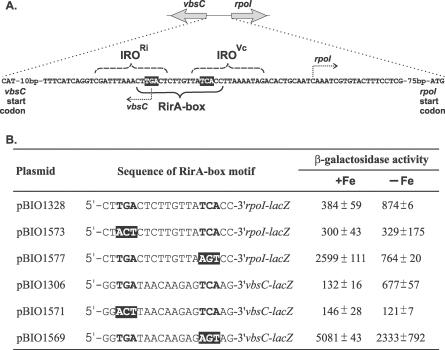
Figure 5. Validation of the Predicted RirA Recognition Motif in R. leguminosarum by Site-Directed Mutagenesis.
(A) RirA-box in the common intergenic region of the RirA-regulated vbsC and rpoI genes in R. leguminosarum. The sequence of this region is shown where the transcription start sites are in bold and marked by arrows. The previously identified IRO-boxes for vbsC and rpoI [41] are under the dashed line brackets. The highly conserved “TGA” and “TCA” in the newly described RirA-box are highlighted.
(B) Effect of mutating the conserved regions of the RirA-boxes on Fe-responsive expression of rpoI-lacZ and vbsC-lacZ transcriptional fusions. The previously described [41] plasmids pBIO1328 and pBIO1306 are based on the wide host-range promoter probe plasmid pMP220 [80] and contain the promoter and regulatory regions of rpoI and vbsC, respectively, fused to its promoter-less lacZ gene. In addition, four new sets of mutant derivatives were made, in which the conserved “TGA” and “TCA” sequences of the RirA-box were substituted, using methods described by Yeoman et al. (2004). Mutant derivatives of pBIO1328 and pBIO1306 with substitutions of the conserved TGA and TCA sequences of the RirA-box were made using the Stratagene ExSite PCR-based Site-directed Mutagenesis kit, with each of these two plasmids being used as template and a suitable oligonucleotide as the mutagenic primer. The mutated forms are shown with dark backgrounds. Each of the six plasmids was individually mobilized into wild type R. leguminosarum. Transconjugants were grown in Fe-replete and Fe-depleted medium and assayed in triplicate for β-galactosidase activity as in Wexler et al. [81].