Fig. 1.
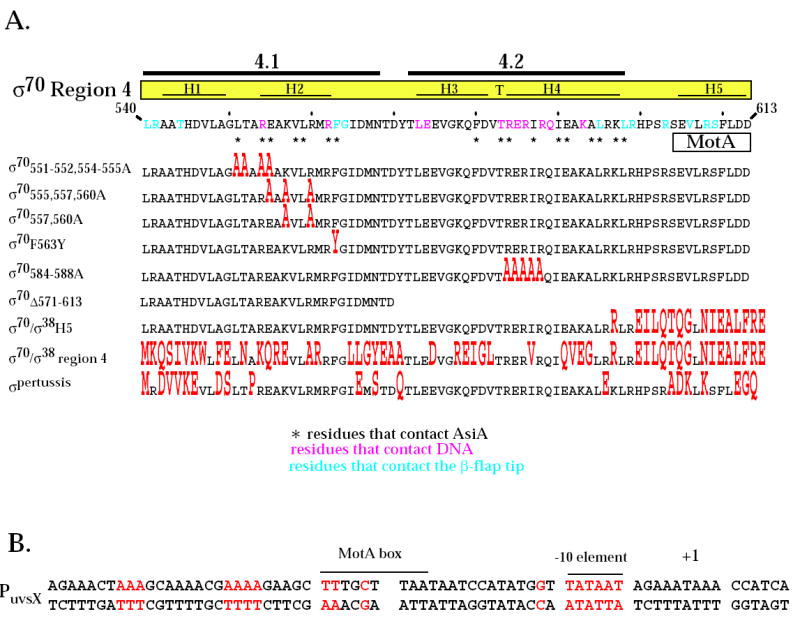
Region 4 of wild type σ70 and mutant σ proteins and the T4 middle promoter PuvsX. A. The C-terminal amino acid sequence of σ70 is shown from residues 540 to 613. Residues in pink contact the -35 element of E. coli promoter DNA 8 while residues in blue contact the β-flap tip 11; 12; 13; 45. Every tenth residue is marked with a small vertical line. Above the sequence is shown the locations of regions 4.1 and 4.2 1 and the positions of the α-helices H1, H2, and H5 and the helix-turn-helix H3-T-H4 structures observed in region 4 of the primary σ of T. aquaticus complexed with -35 element DNA 8. Residues that contact AsiA in the AsiA/σ70 region 4 structure 30 are designated with an asterisk and the region of the MotA contact site 20 is indicated. Below are shown the region 4 sequences of the mutant σ proteins, with residues that differ from σ70 in red. B. The sequence of PuvsX from −61 to +9 is shown with the start of transcription indicated as +1. The locations of the σ70 –10 element and the MotA box are indicated. Sequences within PuvsX that match the canonical polymerase elements σ70 -10 element (TATAAT); σ70 extended -10 element (-15T, -14G); σ70 -35 element (TTGACA); and α UP element (AAAa/ta/tTa/tTTTTnnAAAA) are in red.
