Fig. 5.
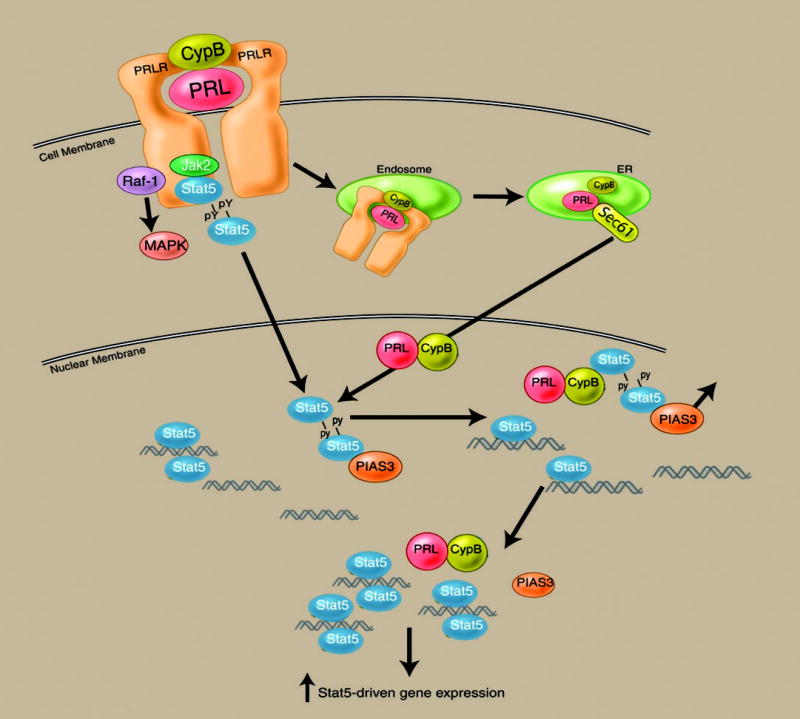
Nuclear actions of the PRL/CypB complex. After endocytosis mediated by the PRLR, the PRL/CypB complex is retrotranslocated to the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi, where the complex associates with the Sec61 transporter. After transport into the cytoplasm, the nuclear translocation signal sequence in the N terminus of CypB facilitates nuclear import. Within the nucleus, the PRL/CypB encounters the Stat5 dimer. Stat5, when bound to the endogenous pool of PIAS3 repressor, is unable to bind to its corresponding DNA promoter sequences. Binding of the PRL/CypB complex to the Stat5 dimer results in the release of PIAS3 (an event requiring the isomerase activity of CypB), enabling Stat5 to engage its DNA binding sequence. The binding of DNA by the Stat5 dimer results in the release of the PRL/CypB complex. Blockade of the nuclear retrotransport of PRL or inactivation of the isomerase activity of CypB significantly down-modulates PRL-driven gene expression and function.
