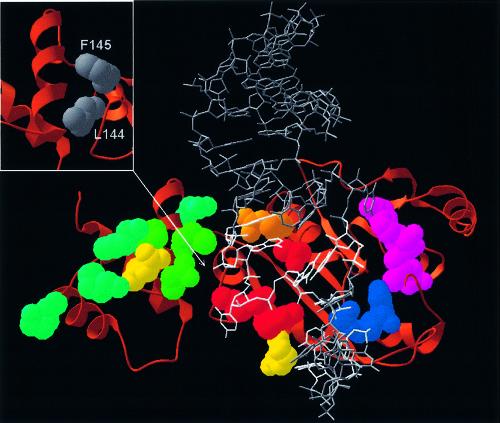
Figure 4.
Speculative model of ErmC′–RNA interactions (the atomic coordinates in the PDB format are available as Supplementary Material and from the website ftp://genesilico.pl/iamb/models/Erm/). The protein is shown in the ‘ribbons’ representation, with experimentally studied residues shown in the ‘spacefill’ representation, colored according to their importance (see the caption to Fig. 2). The model of the RNA substrate 32mer is shown in gray, the target adenosine (A2085) is shown in red, nucleosides important for protein–RNA interactions (13–16) are shown in white. Note that all key RNA-binding residues are located in the large, catalytic (AdoMet-binding) domain. Small panel (upper left corner): hydrophobic residues of the N-terminal domain, which stabilize the structure of the RNA-binding region and may be exposed to the solvent if the C-terminal domain is deleted.