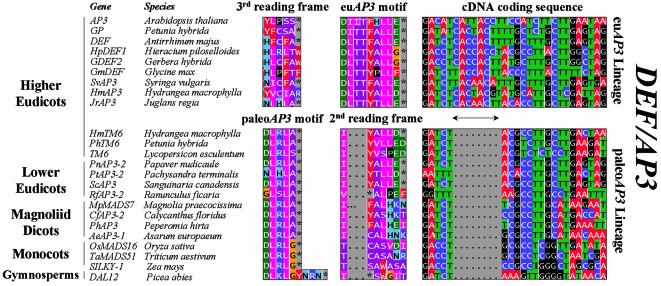
Figure 1.
Alignment of paleoAP3 and euAP3 C-terminal motifs present within the DEF/AP3 subfamily. Although protein sequences belonging to the DEF/AP3 subfamily display extensive homology almost along their entire length (not shown), two lineages can be distinguished on the basis of their completely different C-terminal motifs (columns indicated with paleoAP3 and euAP3 motifs). In contrast, the cDNA fragments encoding the conserved motifs align very well (right column) upon the introduction of a gap of eight base pairs in the coding sequences of paleoAP3 lineage members. The euAP3 motif, which is uniquely present in DEF/AP3 subfamily members isolated from higher eudicots, may thus have originated by a frameshift mutation caused by the eight base pair insertion (indicated by a double headed arrow) into a paleoAP3 ancestral gene. This is illustrated by the second reading frame translation of paleoAP3 members (indicated with 2nd reading frame), which resembles the euAP3 motif. For details on the 3rd reading frame of the euAP3 motif, we refer to the text. A full set of analyzed sequences is presented in the Supplementary Material.