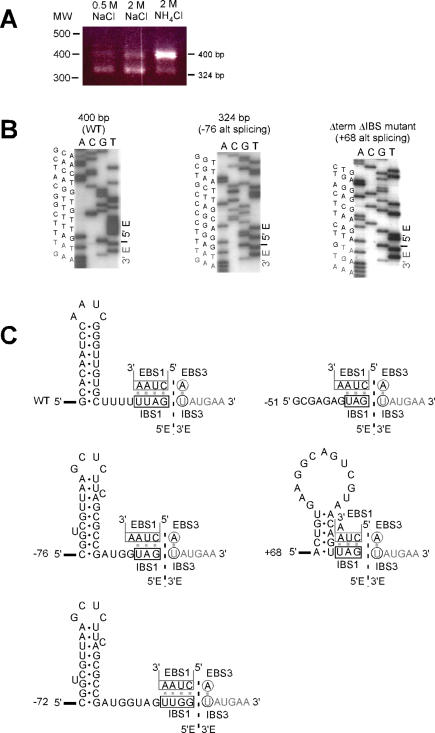
Figure 3.
Cognate and alternative exon ligation events during in vitro splicing reactions. (A) RT–PCR of exon junctions produced in self-splicing reactions. Self-splicing was under standard conditions with 2 M NH4Cl, or with 0.5 or 2 M NaCl. RT–PCR detected two splicing products of 400 bp and 324 bp, whose proportions varied with ionic conditions. (B) Sequencing of ligated exon products. Sequences are shown for the exon-exon junctions of the 400 bp and 324 bp bands in Panel A, and also for the major ligation product formed for the ΔterminatorΔIBS1 mutant described in Figure 4. (C) Sequences and structures of ligated exons. Structures are shown for: the exon–exon products of a cognate splicing reaction (WT); the upstream alternative splicing events at −76, −72, and −51 (relative to the exon–intron junction); and the internal splicing event +68 (relative to the exon–intron junction). EBS1 and EBS3 interactions are drawn above the exon sequences. The +68 stem–loop is present in the native secondary structure, although recognition of the stem may require unpairing of α–α′.