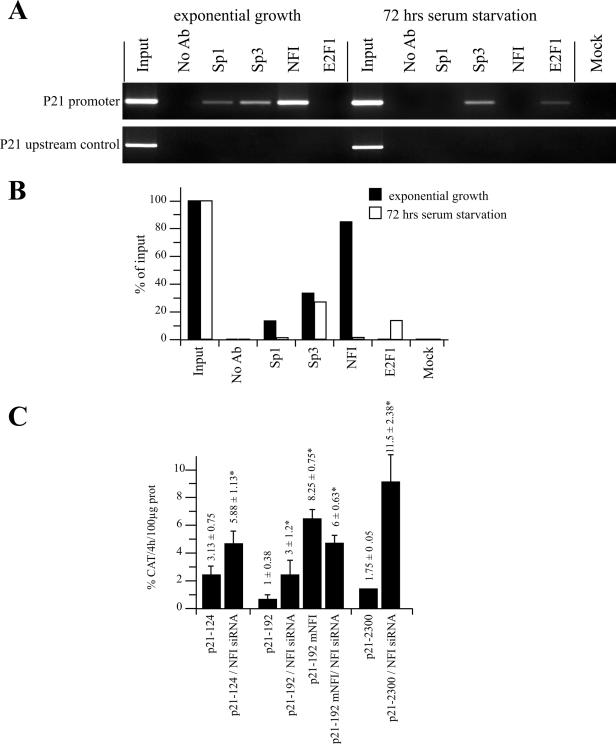
Figure 7.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation of NFI and RNAi assays in HSFs. (A) ChIP assays were performed on HSFs in an exponential state of growth or after 72 h of serum starvation. Chromatin was isolated and immunoprecipited with antibodies directed against the transcription factors Sp1, Sp3, NFI and E2F1. PCR of the p21 gene promoter was then carried out on the ChIP samples along with a ‘no antibody’ control (No Ab) that contains chromatin but no antibody, an ‘input’ sample corresponding to 0.2% of the total input chromatin, and a ‘mock’ sample that does not contain chromatin. PCR amplification of a gene segment located ∼2000 bp upstream from the p21 promoter was also conducted on the same sample as a negative control for all immunoprecipitates. (B) Graphical representation of the amount of specific PCR products expressed as the percentage of antibody binding versus the amount of PCR product obtained using a standardized aliquot of input chromatin. The signal in the no-antibody lane corresponds to the non-specific binding background and was subtracted from each sample. (C) RNAi was performed using a combination of siRNA complementary to the NFI-A, -B, -C and -X transcripts. The p21 promoter-bearing recombinant constructs p21–124, p21–192 and p21–2300, and the derivative from p21–192 that comprise a mutated NFI site (p21–192 mNFI) were transfected together with either the siRNA silencer negative control or with the combination of NFI siRNA duplexes (siNFI) into subconfluent HeLa cells. Cells were harvested and CAT activities determined. *CAT activities that are statistically different from those obtained with the p21 promoter constructs transfected solely with the siRNA silencer negative control (P < 0.05; paired samples, t-test).