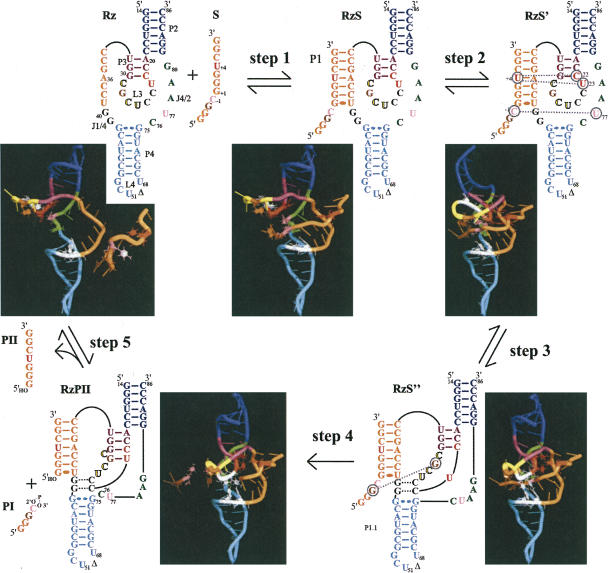
FIGURE 7.
Folding pathway of an HDV ribozyme. Step 1: formation of the RzS complex (i.e., the P1 stem). Step 2: structural rearrangement involving the middle of the P1 stem that orientates the substrate in the catalytic center of the RzS′ complex. Step 3: formation of the P1.1 pseudoknot yielding a productive RzS″ complex. Step 4: cleavage reaction coupled to the fast release of PI. Step 5: dissociation of the RzPII complex into PII and free Rz. The P2 and P4 stems are blue and cyan, while the P1 stem and the substrate are orange. The internal P3 stem and the L3 loop are purple and yellow, respectively. The bases are represented by cylinders except for the stacked nucleotides (red: U + 4, C22, and U23; pink: SC-1 [scissile phosphate] and U77; brown: SG-2 and G28; and, C76 [catalytic cytosine] and the nucleotides involved in the P1.1 stem are white [in black in the 2D scheme]). All water atoms were removed for clarity.