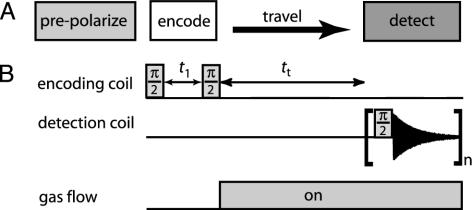
Fig. 1.
(A) The basic schematic and pulse sequence of remote detection is shown. Remote detection begins with a prepolarization step (26), followed subsequently by the three essential parts of the pulse sequence. These parts are the encoding of spectral or image information at one location, the transfer to a different location, and detection in the new location. (B) The pair of π/2 pulses are separated by t1. The second π/2 pulse stores the evolved magnetization onto the ±z-direction. The stored magnetization is transferred to another location during tt and finally detected with a third π/2 pulse. The encoding time, t1, is incremented by the indirect dimension dwell time to map out NMR information in a point-by-point fashion.