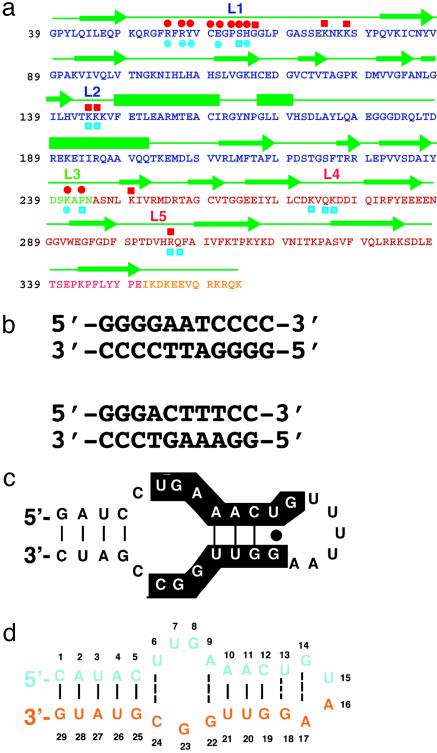
Fig. 1.
Sequence features of p50 RHR and its DNA and RNA targets. (a) Sequence of the RHR of murine p50. Single-letter amino acid codes for the NTD, DD, linker, and flexible region at the C terminus are denoted by blue, green, red, and yellow, respectively. Green arrows denote residues in β-strands, and bars are α-helices. The nucleic acid-binding loops L1, L2, and L3 are shown. Residues of p50 that contact RNA bases through hydrogen bonds (red circles) and backbone phosphates (red squares) are shown above the protein sequence. The DNA base-specific (blue circles) and backbone (blue squares) contacts are denoted below the protein sequence. (b) κB-DNA sequences that preferentially bind the p50 homodimer (Upper) and p50/p65 heterodimer (Lower) are shown. The 11-mer κB-DNA sequence (Upper) is located in the promoter of the H2 gene and binds p50 RHR homodimer. The 10-mer κB-DNA sequence (Lower) is located in the promoter of the Ig-κ light-chain gene and binds p50/p65. (c) The 31-nt RNA aptamer originally identified by in vitro-selection for binding to (p50)2. Nucleotides conserved among selected aptamer variants are highlighted. (d) The optimized 29-nt RNA aptamer used in the cocrystallization experiment.