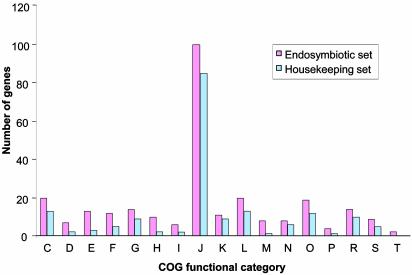
Fig. 3.
Distribution of the putative minimum gene set for insect endosymbiotic life in nonredundant functional categories and its comparison with M. genitalium. The endosymbiotic set corresponds to the 278 protein-coding genes shared by the five insect endosymbiont genomes. The housekeeping set corresponds to the 179 genes with a putative homologue in M. genitalium. Clusters of orthologous genes categories correspond to: C, energy production and conversion; D, cell division and chromosome partitioning; E, amino acid transport and metabolism; F, nucleotide transport and metabolism; G, carbohydrate transport and metabolism; H, coenzyme metabolism; I, lipid metabolism; J, translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; K, transcription; L, DNA replication, recombination and repair; M, cell envelope biogenesis, outer membrane; N, cell motility and secretion; O, posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; P, inorganic ion transport and metabolism; R, general function predicted only; S, function unknown; and T, signal transduction mechanisms.