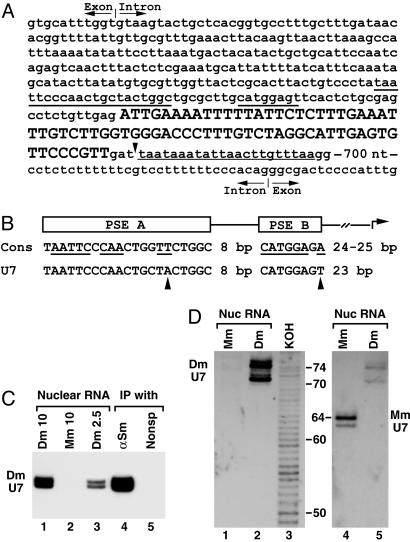
Fig. 3.
Cloning and detection of Drosophila U7 snRNA. (A) The gene for Drosophila U7 snRNA is nested in the intron of the Eip63E gene. The cloned 71-nt cDNA of Drosophila U7 snRNA is shown in uppercase letters and the sequence retrieved from the Drosophila genome is shown in lowercase letters. The 71-nt sequence is followed by GAT, likely included in the longer form of the U7 snRNA. The putative 3′-end signal is underlined with the thin line. Underlined with the thick lines are the two promoter elements, PSE A and B. A part of the intronic sequences surrounding the U7 gene and both the 5′-splice site (top) and the 3′-splice site (bottom) are shown. (B) Comparison of the consensus sequence for the PSE A and B promoter elements found in Drosophila genes for U1, U2, and U4 snRNAs (Cons) with the Drosophila U7 snRNA gene. Conserved nucleotides are underlined, and the nucleotides in the U7 promoter that differ from the consensus are indicated with arrowheads. (C) RNA isolated from 10 or 2.5 μlofa Drosophila nuclear extract (lanes 1 and 3), 10 μl of a mouse nuclear extract (lane 2), or RNA precipitated from 50 μlof the Drosophila nuclear extract by either anti-Sm Ab (lane 4) or a control mAb (lane 5) were resolved in 8% denaturing gels and analyzed by Northern blotting by using the anti-Drosophila U7 probe. (D) Nuclear RNA from mouse myeloma cells (lanes 1 and 4) or Drosophila Kc cells (lanes 2 and 5) was resolved in a high-resolution denaturing gel and analyzed by Northern using the anti-Drosophila U7 probe (Left) followed by hybridization with the anti-mouse U7 probe (Right). Lane 3 contains a ladder of RNA fragments differing in length by 1 nt generated from a 5′-end-labeled 86-nt RNA by partial potassium hydroxide hydrolysis (not shown in Right). The numbers indicate the length of RNA fragments in nucleotides.