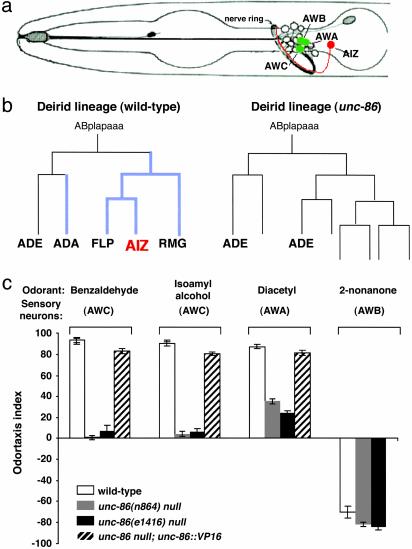
Fig. 1.
Effects of unc-86-null mutations on the olfactory system. (a) A schematic representation of the position of the AIZ interneurons and the olfactory sensory neurons AWA, AWC, and AWB. Each type of neuron is a bilateral symmetric pair; a lateral view is shown. The drawing is adapted from Starich et al. (36). (b) AIZ are the only neurons in the odor-sensation neuronal pathway affected by unc-86 mutations. UNC-86 expression is initiated in the neuroblasts of the lineage (10). The unc-86-null mutation transforms the neuroblast cell fates and AIZ are not generated (9). Cells expressing UNC-86 are indicated by thickened lines. (c) The unc-86-null mutants n846 and e1416 are defective in response to odor attractants, but respond as well as wild-type animals to odor repellents. The unc-86::VP16 fusion transgene can restore unc-86-null mutant odor-attractant responses.