Abstract
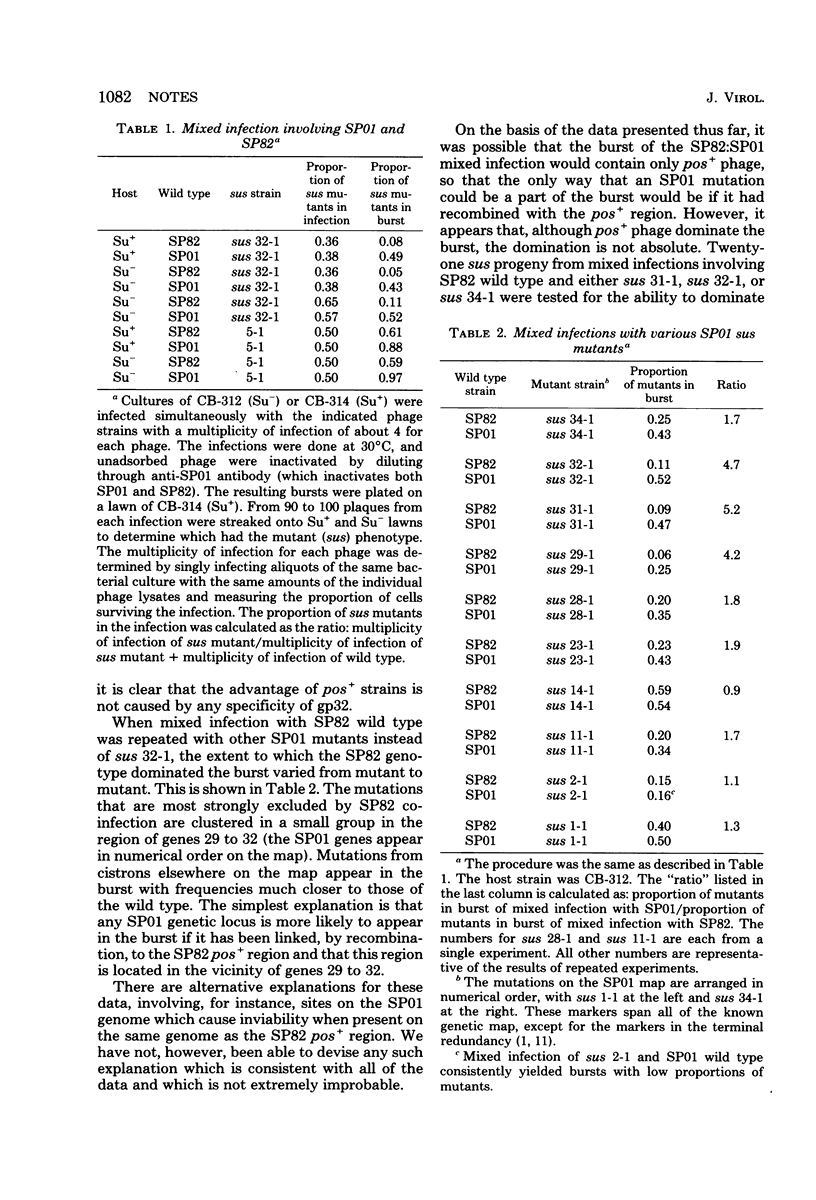
In mixed infections with Bacillus subtilis phages SP82 and SP01, the SP82 genotype is predominant among the progeny. This predominance is determined by a specific region of the genome, the pos region, which apparently is located near genes 29 to 32 (by the SP01 numbering system). Recombination between SP82 and SP01 yields phage which have both the SP82 pos region and an SP01 mutation. This mutation then behaves in mixed infection as if it were part of an SP82 genome.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cregg J. M., Stewart C. R. Terminal redundancy of "high frequency of recombination" markers of Bacillus subtilis phage SPO1. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):530–541. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Geiduschek E. P. RNA synthesis during bacteriophage SPO1 development: six classes of SPO1 RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassberg J., Franck M., Stewart C. R. Initiation and termination mutants of Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPO1. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):147–152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.147-152.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassberg J., Franck M., Stewart C. R. Multiple origins of replication for Bacillus subtilis phage SPO1. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassberg J., Slomiany R. A., Stewart C. R. Selective screening procedure for the isolation of heat- and cold-sensitive, DNA replication-deficient mutants of bacteriophage SPO1 and preliminary characterization of the mutants isolated. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.54-60.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. M., Laman D. Organization of gene function in Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SP82G. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):1033–1046. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.1033-1046.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R. Bacteriophages of Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):257–315. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.257-315.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R. Mixed infections of Bacillus subtilis involving bacteriophage SPO2c 1 . J Virol. 1973 Jan;11(1):25–34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.1.25-34.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrie J. M., Downard J. S., Whiteley H. R. Bacillus subtilis bacteriophages SP82, SPO1, and phie: a comparison of DNAs and of peptides synthesized during infection. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):725–737. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.725-737.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levner M. H., Cozzarelli N. R. Replication of viral DNA in SPO1-infected Bacillus subtilis. I. Replicative intermediates. Virology. 1972 May;48(2):402–416. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Yanagida T., Fujita D. J., Olsson-Wilhelm B. M. The genetics of bacteriophage SPO1. Biken J. 1972 Jun;15(2):81–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palefski S., Hemphill H. E., Kolenbrander P. E., Whiteley H. R. Dominance relationships in mixedly infected Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):594–601. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.594-601.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pees E. Bacteriophage T4 mutants unable to exclude gene 56 of T2 from the progeny of crosses. Mutat Res. 1970 Mar;9(3):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(70)90136-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pees E., De Groot B. Partial exclusion of genes of bacteriophage T2 with T4-glucosylated DNA in crosses with bacteriophage T4. Genetica. 1970;41(4):541–550. doi: 10.1007/BF00958933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero J., Hannett N. M., Talkington C. Restriction cleavage map of SP01 DNA: general location of early, middle, and late genes. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):156–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.156-171.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve J. N., Mertens G., Amann E. Early development of bacteriophages SP01 and SP82G in minicells of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 5;120(2):183–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. L., Huskey R. J. Partial exclusion between T-even bacteriophages: an incipient genetic isolation mechanism. Genetics. 1974 Dec;78(4):989–1014. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.4.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. In vivo and in vitro transcription by ribonucleic acid polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1483–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. R., Click B., Tole M. F. DNA replication and late protein synthesis during SP82 infection of Bacillus subtilis. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):653–663. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90419-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffaut N., Revet B., Soulie M. O. Etude comparative des DNA de phages 2C, SP8*, SP82, phi e, SP01 et SP50. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Aug;15(2):391–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley H. R., Kolenbrander P. E., Hemphill H. E. Mixed infections of Bacillus subtilis involving bacteriophages SP82 and beta 22. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1463–1469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1463-1469.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


